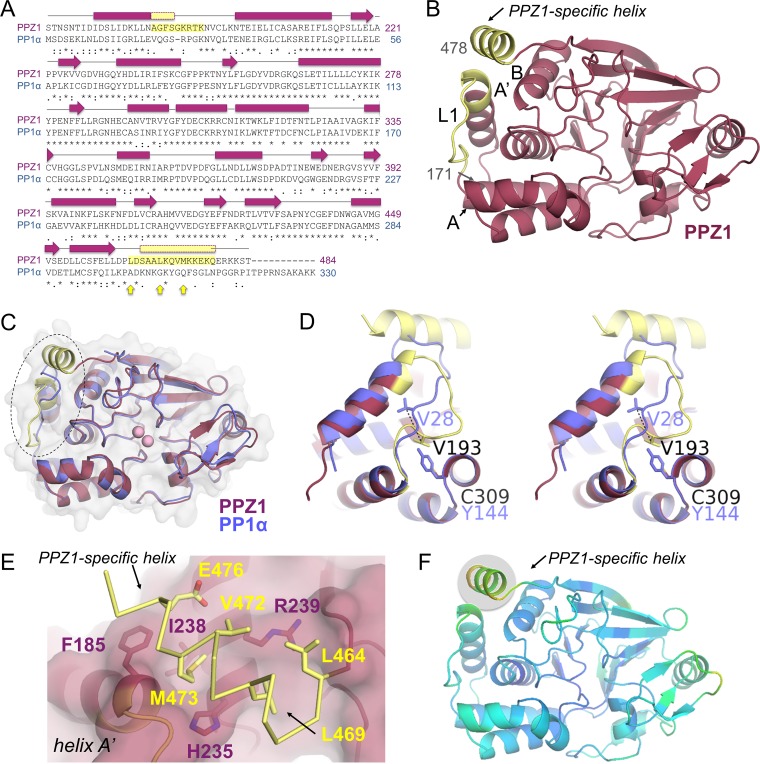
FIG 2 .
The PPZ1-specific C-terminal helix. (A) Sequence alignment of CaPPZ1 (pink) and Homo sapiens PP1 (HsPP1α [blue]) with the observed secondary structural elements indicated above the sequence. Identical residues are indicated by a star, similar residues are indicated by a colon, less similar residues are indicated by a period, and dissimilar residues are indicated by a blank space. Resides from loop 1 (L1) and the PPZ1-specific helix are highlighted in yellow. Arrows (yellow) indicate the hydrophobic residues in the PPZ1-specific helix that are not present in PP1α. (B) The structure of PPZ1 is shown with the secondary structural elements discussed in the text labeled. (C) Overlay of PPZ1 (pink and yellow, as in panel B) and PP1α (blue). The change in conformation of loop L1 between the two structures is indicated by a dashed circle. (D) Stereo image of the overlay between L1 from PPZ1 and PP1α, colored as in panel C. (E) Interactions between the PPZ1-specific C-terminal helix (yellow) and the widened PPZ1-specific helix binding pocket (coral). Residues that make key interactions are shown as sticks and labeled. (F) PPZ1 colored according to residue B-factors, with yellow and green shading indicating higher B-factors.