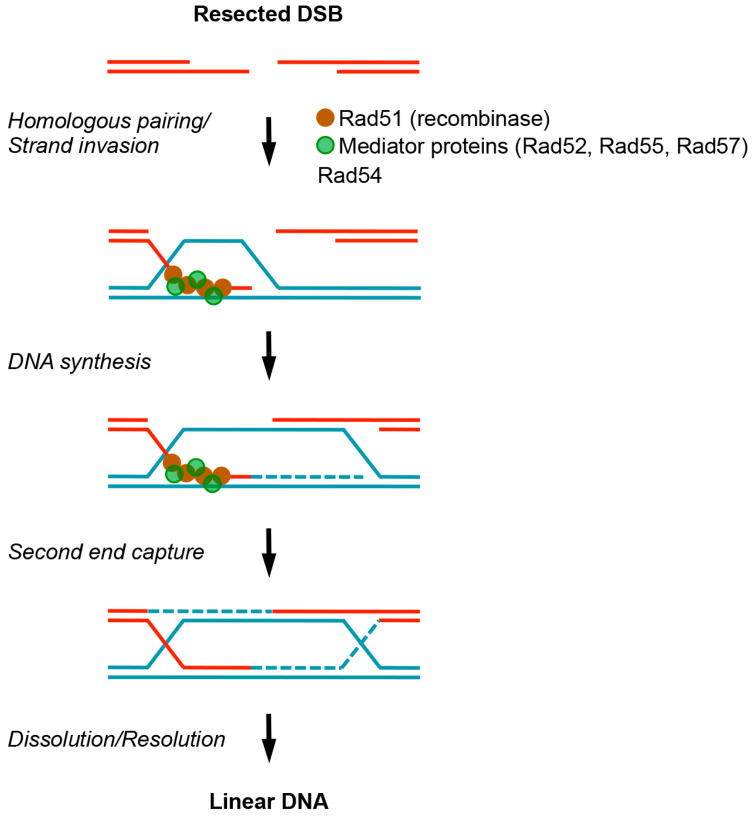
Figure 1.
Simplified schematic of homologous recombination repairing DNA breaks. Recombinational repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is initiated by resection away from the break, generating ssDNA. Rad51 then forms filaments along ssDNA with the help of mediator proteins, and then together with additional factors (including Rad54), they facilitate the Rad51-ssDNA filament in homology search and strand invasion into homologous sequences. This leads to the formation of DNA D-loop structures. After DNA synthesis of the invading strand, second end capture generates double Holliday junctions, which can then be processed by dissolution and resolution pathways, as described in the text. For further details, see [6,7].