Figure 4.
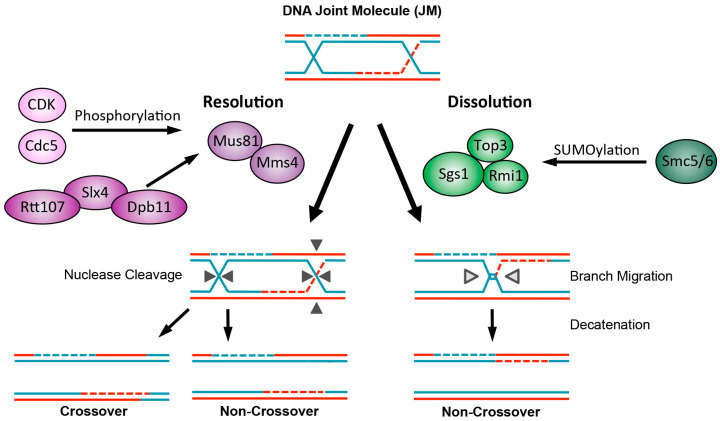
Two pathways for DNA joint molecule (JM) processing are regulated by phosphorylation and SUMOylation. Recombinational repair produces intermediates in the forms of JMs, such as double Holliday junctions, which are processed by two mechanisms: dissolution and resolution. In JM dissolution, the combined branch migration and decatenation activities of the Sgs1-Top3-Rmi1 complex process JMs into non-crossover products. The function of Sgs1-Top3-Rmi1 in this process is promoted by Smc5/6-mediated SUMOylation, likely in the S and G2 phases. In JM resolution, several nucleases, such as Mus81-Mms4, directly cleave JMs, resulting in a mixture of crossover and non-crossover products. Phosphorylation of Mms4 by CDK and Cdc5, in conjunction with the Slx4-Dpb11-Rtt107 scaffold complex, promotes Mus81-Mms4 activity in mitosis.