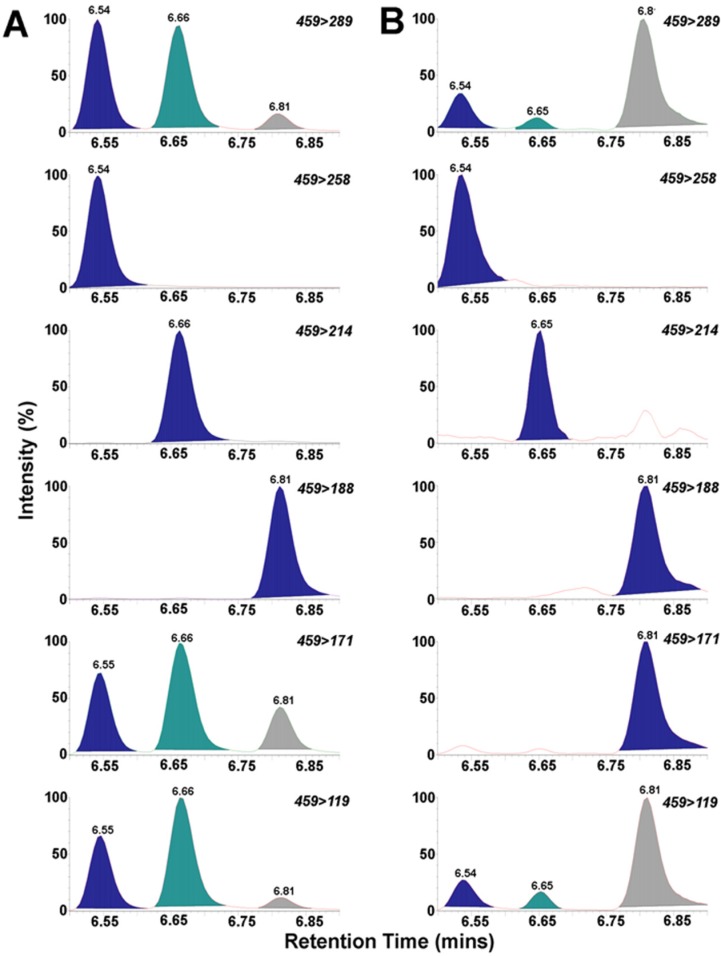
Figure 2.
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) detection and conformation of BMAA in shark fins. (A) Chromatograms depicting detection of ACQ derivatized standards of BMAA, and structural isomers N-(2-aminoethyl) glycine (AEG) and 4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB); (B) UPLC-MS/MS chromatograms of BMAA detection in fins from Australian sharks. The diagnostic selected reaction monitoring (SRM) transitions of the parent ion m/z 459 to daughter ions 289, 171 and 119 are common to all three isomers. The BMAA (blue) peak is selectively identified at 6.55 min by the transition 459 > 258. AEG (green) is selectively identified at 6.66 min by the transition 459 > 214. DAB (grey) is selectively identified at 6.81 min by the transition 459 > 188.