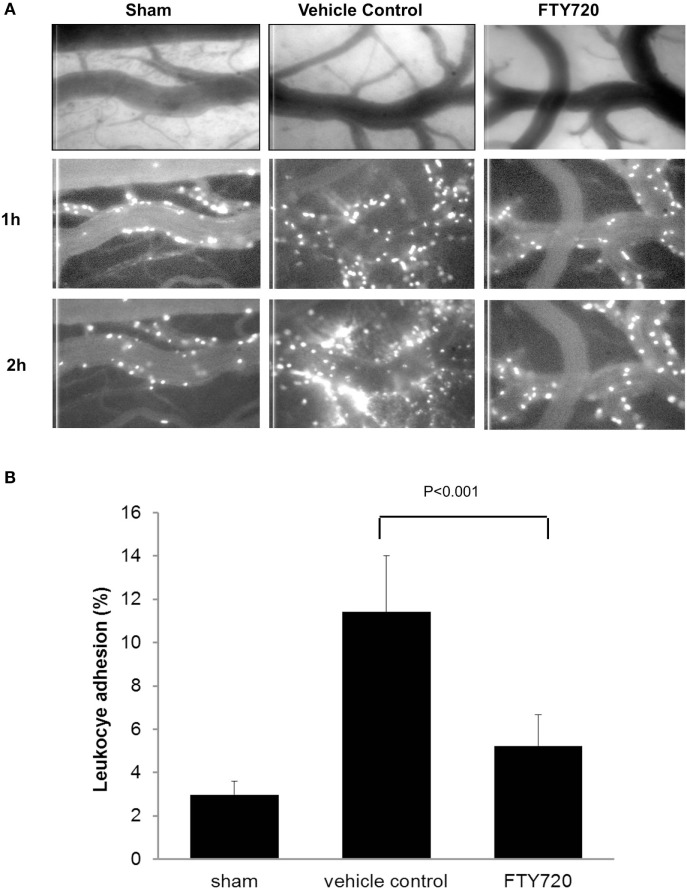
Figure 3.
Assessment of neuroinflammation after cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Male adult Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) for 60 min followed by reperfusion. Three hours after reperfusion, animals were treated with vehicle or 0.5 mg/kg FTY720 intraperitoneally. Leukocyte adhesion to pial venules was determined 24 h after reperfusion by intravital microscopy using rhodamine 6G-labeled autologous leukocyte as previously described (46). (A) Representative pictures of the vessel anatomy and the trafficking of leukocytes 1 and 2 h after leukocyte labeling with Ro6G in sham, vehicle control, and FTY720-treated animals. (B) Quantification of leukocyte adhesion, expressed as the percentage of the vessel area occupied by adherent leukocytes measured 1 h after leukocyte labeling. The MCAo-vehicle group demonstrated a significant increase in vascular leukocyte adhesion at 24 h post reperfusion compared to sham. The treatment with FTY720 decreased the adherence of leukocytes to pial vessels by almost 60%. Significance determined using an unpaired t-test. Means ± SD (n = 5).