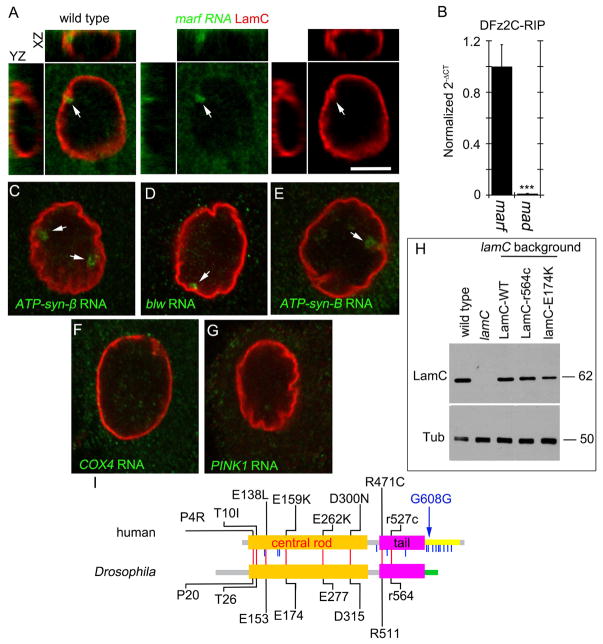
Figure 1. Association of marf mRNA with DFz2C and nuclear LamC foci.
(see also Figure S1)
(A, C–G) FISH of a larval body wall muscle preparations using a (A) marf (C) ATP-syn-β, (D) blw, (E) ATP-syn-B, (F) cox4, (G) pink1 DNA probe and antibodies to LamC. Arrows denote foci containing mitochondrial transcripts.
(B) Real time PCR of marf and mad after RNA-immunoprecipitation with DFz2C antibody from larval body wall muscles.
(I) Schematic depiction of Drosophila LamC and human LMNA protein structure, indicating conserved (red vertical lines) and non-conserved (blue vertical lines) amino acid residues that when mutated cause progeroid syndromes in humans. Blue arrow indicates the mutation responsible for most HGPS cases.
(H) Western blot of body wall muscle protein extracts from animals of the indicated genotypes probed with antibodies to LamC (top) and tubulin (Tub; bottom). Numbers at the right represent molecular weight in KDa.
***p<0.001 Error bars= SEM. Calibration bar in A, C–G is 6μm.