FIG 1 .
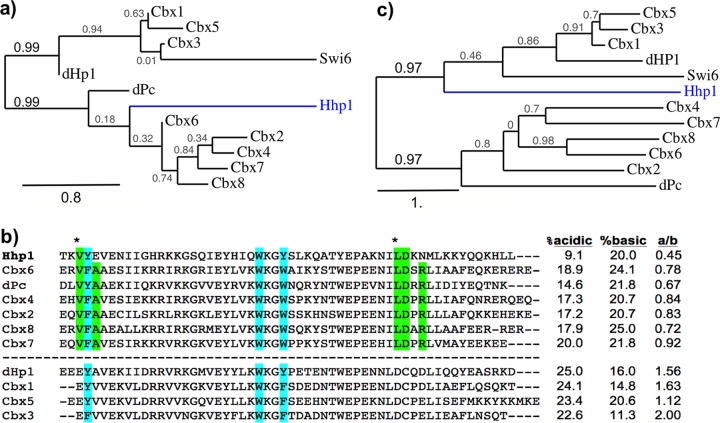
Hhp1 CD is more similar to Pc-type than HP1-type CDs. (a) Phylogenetic analysis of CDs from Tetrahymena HP1 (Hhp1) with dHP1a, Pc, and human homologs. ClustalW alignment (MUSCLE) and the maximum-likelihood method (PhyML 3.0) (52) were used for tree generation, and the results were displayed by using TreeDyn 198.3 (58). The scale bar represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The branch length is proportional to the number of substitutions per site. Swi6 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe is included for evolutionary range. (b) Alignment of CD sequences shown in order of alignment with Hhp1. Green highlighting indicates residues that are important for Pc interactions with H3K27Me3 (9), and asterisks indicate those that distinguish Pc-type affinities for H3K27Me3 binding from HP1-like CDs (groups separated by the dashed line) (11). Light blue highlighting shows the aromatic cage residues responsible for methyl-lysine binding. The percentages of acidic and basic residues and the ratio of acidic to basic residues (a/b) in each CD are shown on the right. (c) Phylogenetic analysis of the entire CD protein sequences aligned in panel b. The scale bar represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. The branch length is proportional to the number of substitutions per site.