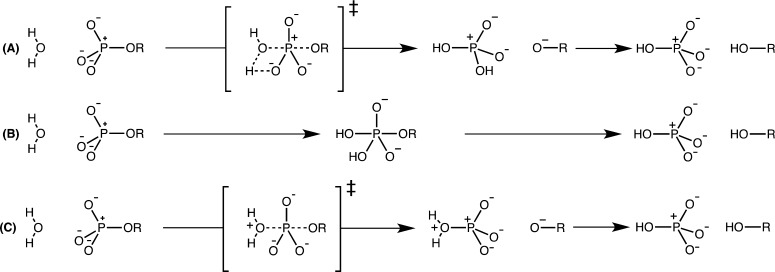
Figure 1.
Hypothetical pathways for the hydrolysis of phosphate monoester dianions considered in this work. (A) A concerted pathway with substrate-assisted nucleophilic attack, in which the attacking water molecule is deprotonated by the substrate at some point along the reaction coordinate. (B) A stepwise pathway in which proton transfer from the nucleophile to the substrate is concerted with nucleophilic attack, leading to a pentacoordinate intermediate that breaks down with concerted proton transfer to the leaving group. (C) A concerted pathway with solvent-assisted nucleophilic attack, in which there is no proton transfer from the nucleophile in the rate-limiting step. This figure was adapted from ref (23).