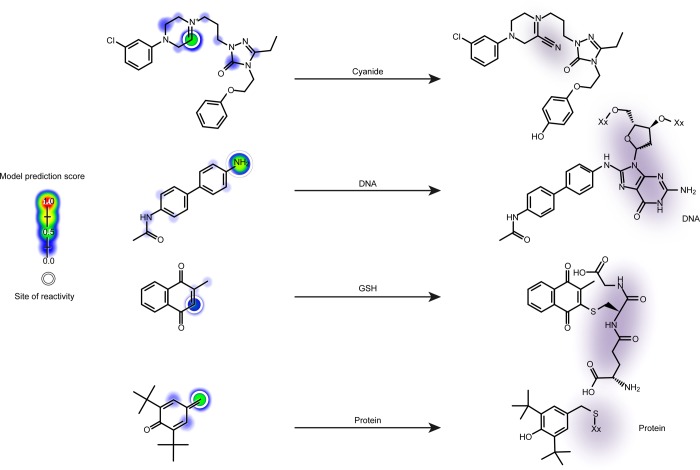
Figure 1.
Examples of the four types of sites of electrophilic reactivity modeled. Predictions by the XenoSite reactivity model are indicated on the left with a colored shading gradient and white circle for each known site of reactivity. These predictions range from zero to one, indicating the probability that an atom is reactive with each of the four nucleophilic targets. From top to bottom, a cyanide conjugation of a nefazodone metabolite,21 a DNA conjugation of N-acetylbenzidine,22 a glutathione (GSH) conjugation of menadione,23 and a protein conjugation of a butylated hydroxytoluene metabolite.24 DNA and protein are inherently structurally diverse, and thus cartoonized macromolecules are depicted, with the rest of each macromolecule represented by “Xx”.