FIGURE 7.
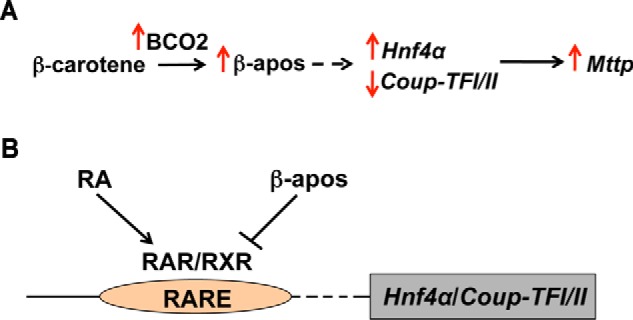
Schematic representation of the proposed model of BC regulation of lipoprotein biosynthesis in placenta. A, in the presence of BC, placental Bco2 transcription (and likely activity) increases, thus enhancing the generation of β-apocarotenoids (β-apos). This metabolite(s) then, directly or indirectly (dashed arrow), increases the transcription of Hnf4α and represses the transcription of Coup-TFI and Coup-TFII, which in turn increase the transcription of Mttp and consequently its activity, ultimately stimulating biosynthesis and transfer of BC-containing lipoproteins toward the fetus. B, β-apocarotenoids antagonize the action of retinoic acid (RA) in regulating, directly or indirectly (dashed arrow), the transcription of Hnf4α and Coup-TFI/II. RAR, retinoic acid receptor.
