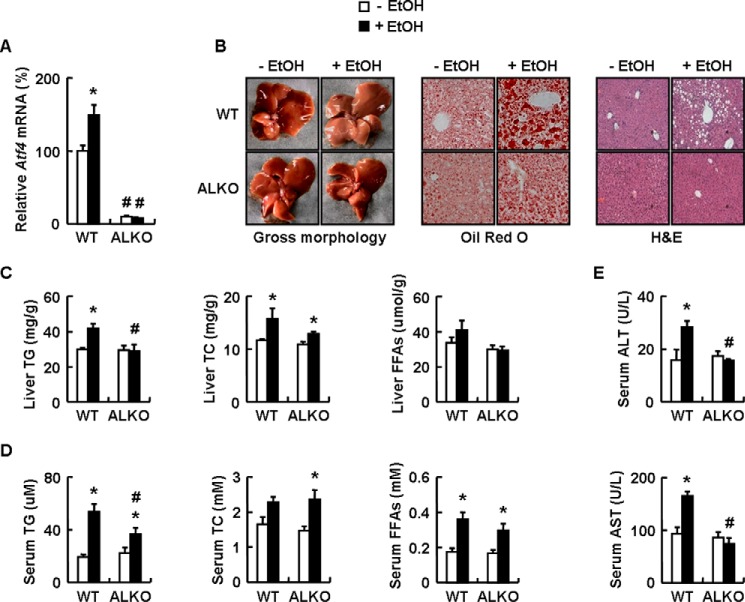
FIGURE 2.
ALKO mice are resistant to ethanol-induced liver steatosis. A–E, WT and ALKO mice were fed a control (−EtOH) or ethanol-containing diet (+EtOH) for 28 days. Means ± S.E. (error bars) shown are representative of at least two independent in vivo experiments, with the number of mice included in each group in each experiment indicated (n = 8). Statistical significance was determined by Student's t test for the effect of with versus without ethanol feeding in WT or ALKO mice (*, p < 0.05) or ALKO mice versus WT mice under ethanol diet or control diet (#, p < 0.05). A, Atf4 mRNA; B, pictures of mouse livers, representative Oil Red O staining, and H&E staining of liver tissues (magnification, ×10); C and D, hepatic or serum TG, TC, and FFA levels; E, serum ALT and AST levels.