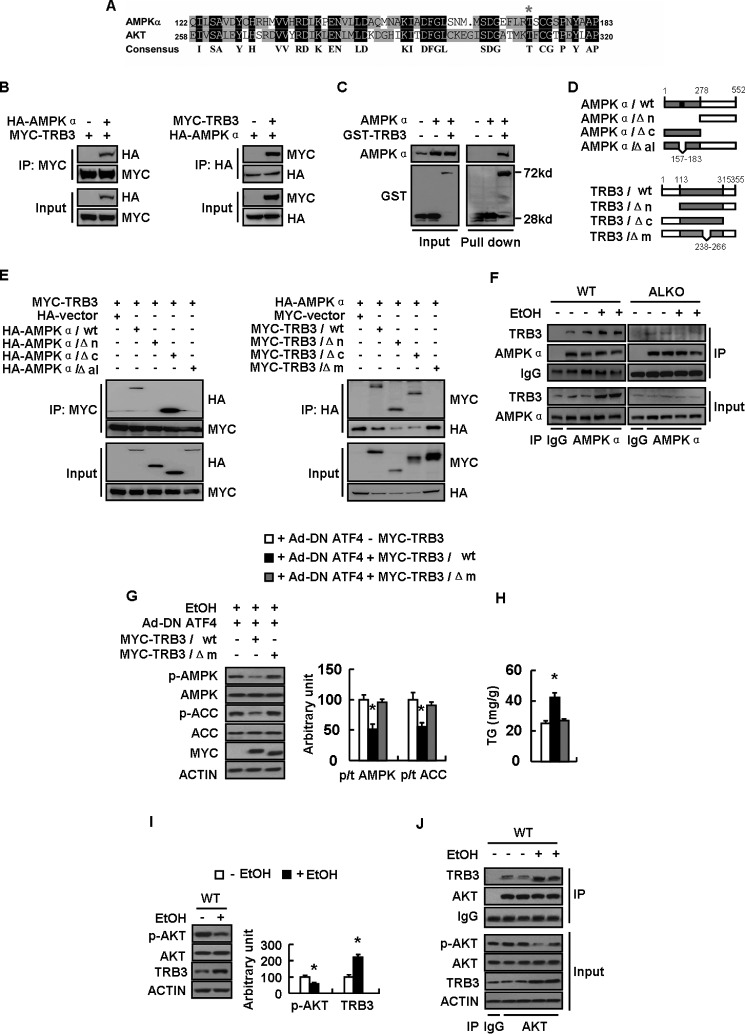
FIGURE 7.
TRB3 directly binds to AMPKα and inhibits its phosphorylation. A, alignment of the amino acid sequences between AMPK alpha and AKT. B–E, a series of constructs of control vector (−MYC-TRB3 or −GST-TRB3) or Myc-tagged (+MYC-TRB3) or GST-tagged total TRB3 (+GST-TRB3) or deletion mutants (as indicated) were cotransfected with the plasmid expressing control vector (−HA −AMPKα) or HA-tagged AMPKα (+HA −AMPKα) or deletion mutants (as indicated) into HEK-293T cells for 24 h. F, WT and ALKO mice were fed a control (−EtOH) or ethanol-containing diet (+EtOH) for 28 days. G and H, primary hepatocytes infected with Ad-DN ATF4 (+Ad-DN ATF4) and transfected with plasmids expressing Myc-TRB3/WT or Myc-TRB3/Δm as indicated for 48 h, followed by treatment with 100 mm ethanol (+EtOH) for 24 h. I and J, WT mice were fed a control (−EtOH) or ethanol-containing diet (+EtOH) for 28 days. Means ± S.E. (error bars) shown are representative of at least three independent in vitro experiments or two independent in vivo experiments, with the number of mice included in each group in each experiment indicated (n = 8). Statistical significance was determined by Student's t test for the effect of Myc-TRB3/WT or Myc-TRB3/Δm versus control plasmid in G and H or with versus without ethanol treatment in I (*, p < 0.05). A, alignment of the amino acid sequences possibly mediating the interaction between AMPKα and AKT; B and E, co-IP assay for the interaction between AMPKα and TRB3; C, GST pull-down assay for the interaction between AMPKα and TRB3; D, schematic representation of TRB3 and AMPKα deletion mutants; F, binding of AMPK and TRB3 in WT and ALKO mouse livers exposed to ethanol or not; G, p-AMPK, AMPK, p-ACC, and ACC protein levels (left, Western blotting; right, quantitative measurements of p-ACC or p-AMPK relative to their total proteins); H, TG contents; I, p-AKT, AKT, and TRB3 protein levels (left, Western blotting; right, quantitative measurements of p-AKT and TRB3 relative to their total protein or actin); J, binding of AKT with TRB3.