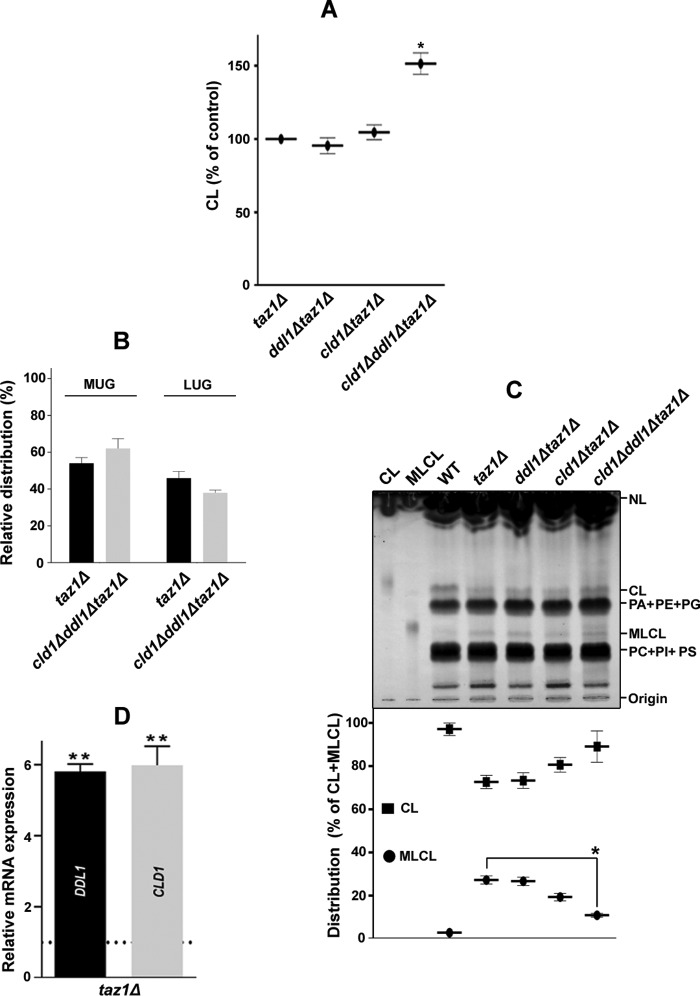
FIGURE 9.
The DDL1 gene and cellular MLCL content. A, effects of the TAZ1, DDL1, and CLD1 genes on the cellular CL content. The lipids that were extracted from the stationary-phase cells (A600 = 25) grown in the presence of [14C]acetate were analyzed on a TLC plate. B, TAZ1, DDL1, and CLD1 genes and molecular species of CL. The molecular species of CL in the cld1Δddl1Δtaz1Δ strain were compared with the taz1Δ control, and the data for the taz1Δ strain were duplicated from Fig. 4A. C, effects of the TAZ1, DDL1, and CLD1 genes on the cellular MLCL content. The lipids that were extracted from the stationary-phase lyophilized cells (50 mg) were resolved on a TLC plate, which was then charred with 10% cupric sulfate in 8% aqueous phosphoric acid for 10 min at 180 °C. The amounts of CL and MLCL were determined relative to the total CL (CL + MLCL). D, analysis of the expression of the DDL1 and CLD1 genes in the taz1Δ strain. The horizontal dotted line represents expression in the WT strain. The values are represented as fold changes. The values are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3), and significance was determined at *, p < 0.05; and **, p < 0.01.