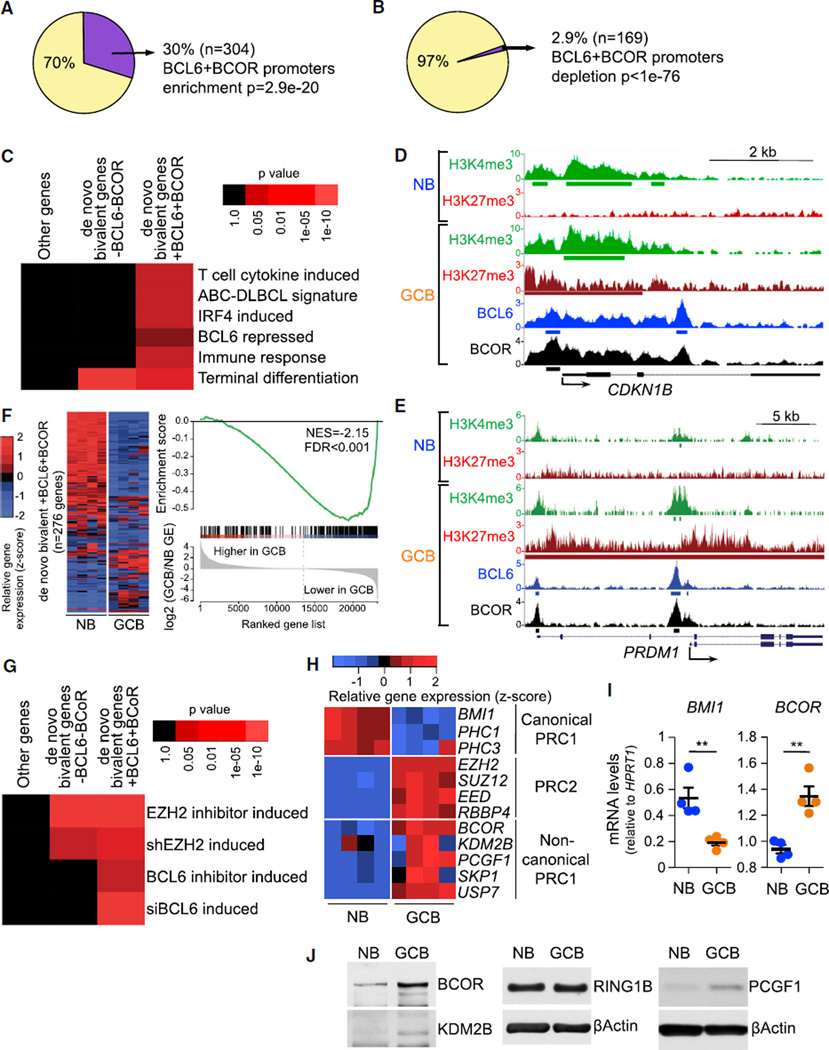
Figure 3. EZH2 and BCL6/BCOR Complexes Are Both Required to Repress Key De Novo GC B Cell Bivalent Promoters.
(A and B) Percentage and number of de novo bivalent promoters (H3K27me3+H3K4me3, n = 1,011) (A) and H3K27me3 monovalent promoters (n = 5,798) (B) overlapping ChIP-seq peaks of BCL6 and BCOR in GC B cells.
(C) Heatmap of over-represented gene categories among genes with BCL6+BCOR-occupied de novo bivalent promoters compared with non-bivalent genes and de novo bivalent genes without BCL6 or BCOR. Enrichment was measured using hypergeometric p values.
(D and E) CDKN1B (D) and PRDM1 (E) gene loci showing H3K4me3, H3K27me3, BCL6, and BCOR ChIP-seq read density in naive B cells (NB) and germinal center B cells (GCB). Green, red, blue, and black bars: H3K4me3, H3K27me3, BCL6, and BCOR peaks, respectively.
(F) Heatmap of the gene expression level and GSEA of de novo bivalent genes with BCL6+BCOR in 4 NB and 4 GCB samples. NES, normalized enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate.
(G) Heatmap of over-represented de novo bivalent genes with and without BCL6- and BCOR-occupied promoters for genes induced by EZH2 or BCL6 inhibitors (2 µM GSK343 for 5 days and 25 µM FX1 for 12 hr) or shRNAs for EZH2 (7 days) or siRNAs for BCL6 (2 days) in OCI-Ly1, OCI-Ly7, SUDHL5, SUDHL6, Farage, WSU-DLCL2, and Pfeiffer DLBCL cell lines. Enrichment measured using hypergeometric p values.
(H and I) Heatmap of the gene expression level (H) and RT-qPCR (I) of canonical and non-canonical PRC1 components in 4 NB and 4 GCB samples. Values in (I) are shown as means ± SEM. t test, **p < 0.01.
(J) Immunoblotting of whole-cell lysates from NB and GCB samples.