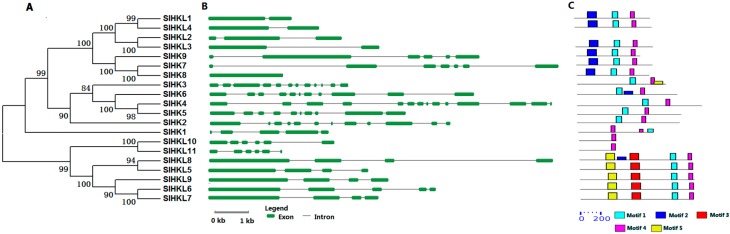
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis, gene structure, and conserved motifs of all HK(L) genes in tomato. (A) The phylogenetic tree of HK(L) proteins. Predicted amino acid sequences of HK(L) proteins were aligned using the Clustal X v1.81 program. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates as implemented in the MEGA 5.0; (B) Gene structure was analyzed using the Gene Structure Display Server online. The green boxes indicate the exons, and lines indicate the introns; (C) Schematic distribution of conserved motifs in the HK(L) proteins. Motif analysis was performed using MEME 4.0 software as described in the methods. The colored boxes represent different motifs in the corresponding position of each HK(L) protein.