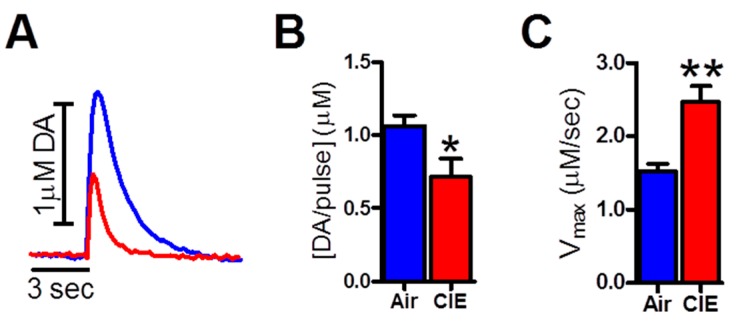
Figure 1.
Chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) exposure reduced dopamine release and increased dopamine uptake in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) core. Representative FSCV traces are overlaid in (A) (Air: blue trace; CIE: red trace); (B) CIE reduced dopamine release in brain slices of the NAc from CIE-exposed mice compared to air-exposed controls; (C) CIE increased dopamine uptake rates (Vmax) in brain slices from CIE-exposed mice compared to controls. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.05 (CIE: chronic intermittent ethanol).