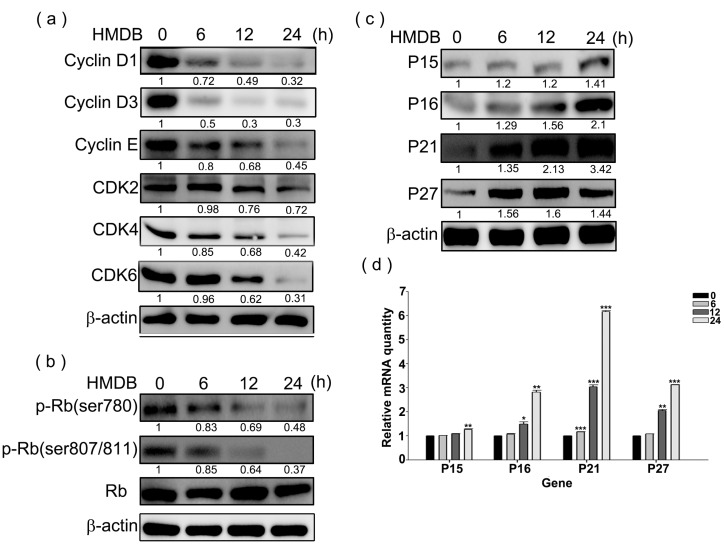
Figure 2.
Effects of HMDB on the expression of G1-related cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and CDK inhibitors (CKIs). (a) Relative protein expression levels of cyclin D1/D3/E, and CDK4/6/2 expressed in the G1 phase; (b) the total and phosphorylated forms of retinoblastoma (Rb) with specific antibodies for each; and (c) the change in the protein expression levels of CKIs (p15, p16, p21, and p27). HeLa cells were exposed to 40 μM HMDB for the indicated times. Then, cellular extracts were harvested and the protein levels were visualized by Western blotting using antibodies against G1 cell cycle regulators as indicated. The β-actin acts as an internal control for evaluating protein loading; and (d) the changes in mRNA expression levels of CKIs, including p15, p16, p21, and p27, by HMDB. The relative amounts of target mRNA, collected from HMDB-treated HeLa cells, were determined by qRT-PCR for the indicated time. All of the results that come from independent experiments three times are expressed as mean ± SE. The relative amounts of protein levels on the Western blots were quantitated with a computerized densitometer (ImageQuant LAS4000 Digital System, GE Healthcare, Uppsala, Sweden) compared to the control group. Values were statistically significant for * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared with the control group (without HMDB treatment).