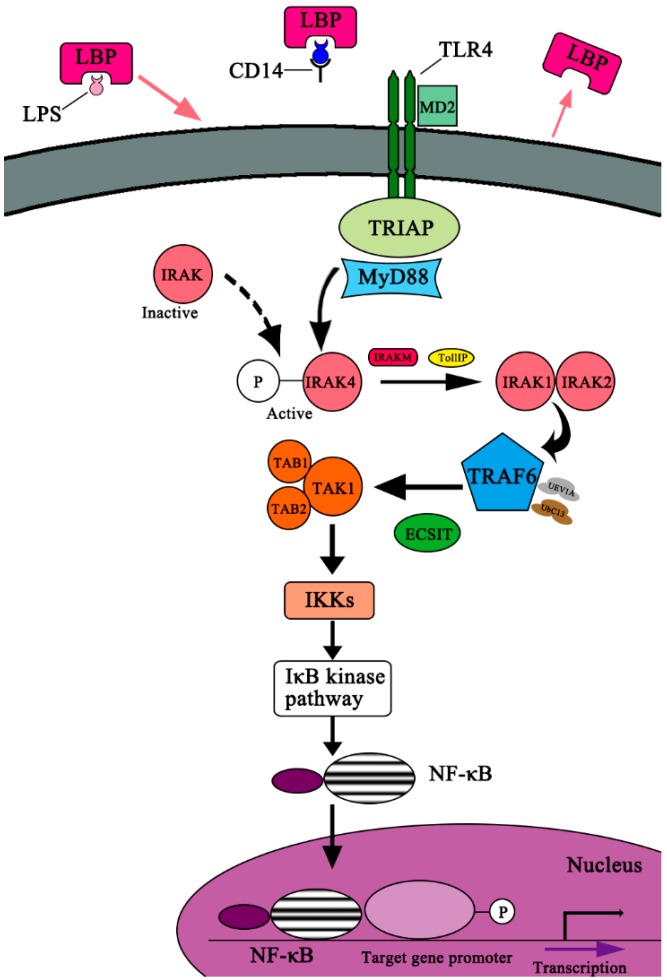
Figure 2.
Diagram of LPS-induced TLR4 signaling. LPS, the breakdown bacterial component, binds to LBP, and then is released from the LPS-LBP complex, and is presented to CD14 and TLR4 on APCs, leading to the activation of TLR4. With the assistance of MD-2, an important component of activated TLR4, termed Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) homologous domain, binds to the C-terminus of cytoplasmic adaptor proteins MyD88, while the death domain (DD) at the N-terminus of MyD88 interacts with intercellular enzyme IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), eventually resulting in the phosphorylation of IRAK and the activation of TNF-α receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF-6). The phosphorylated IRAK binds to the activated TRAF, and the complex activates TGF-β-activated Kinase-1(TAK1), triggering the activation of inhibitor of κ polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells (IκB) kinase, eventually activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. The NF-κB signaling pathway upregulates the expression levels of the target gene. The activated NF-κB signaling initiates the expression of target genes, leading to the damage of target organs. TLR4 = Toll-like Receptor-4; LBP = lipopolysaccharide-binding Protein; TIR = Toll-Interleukin-1-Receptor; TIRAP = Toll-Interleukin-1-Receptor Domain-containing Adapter Protein; MyD88 = Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Protein-88; IRAK = Interleukin-1 Receptor-associated Kinase; IRAKM = Interleukin-1 Receptor-associated Kinase-M; TollIP = Toll-Interacting Protein; TRAF6 = Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-associated Factor-6; UbC13 = Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme-13; UEV1A = Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme E2-Variant-1; ECSIT = Evolutionarily Conserved Signaling Intermediate in Toll Pathways; TAK1 = TGF-β-activated Kinase-1; TAB1 = TAK1-binding Protein-1; TAB2 = TAK1-binding Protein-2; IKKs = Inhibitor of κ Light Polypeptide Gene Enhancer in B-Cells Kinase.