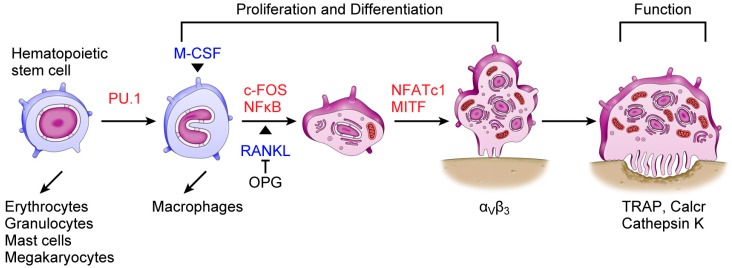
Figure 1.
Schematic view of osteoclast differentiation. Osteoclasts are derived from hematopoietic stem cells. Cytokines macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) are essential for osteoclastogenesis. Binding of RANKL to its receptor, receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK), activates nuclear factor of activated T cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1), which is a master regulator of osteoclastogenesis. NFATc1 works with other transcription factors, such as activator protein-1 (AP-1), PU.1, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) to induce various osteoclast-specific genes, such as TRAP, Calcr, and Cathepsin K. RANK-RANKL interaction is inhibited by the decoy receptor osteoprotegerin (OPG) expressed by stromal cells and osteoblasts. Blue, cytokines essential for osteoclastogenesis; red, transcription factors.