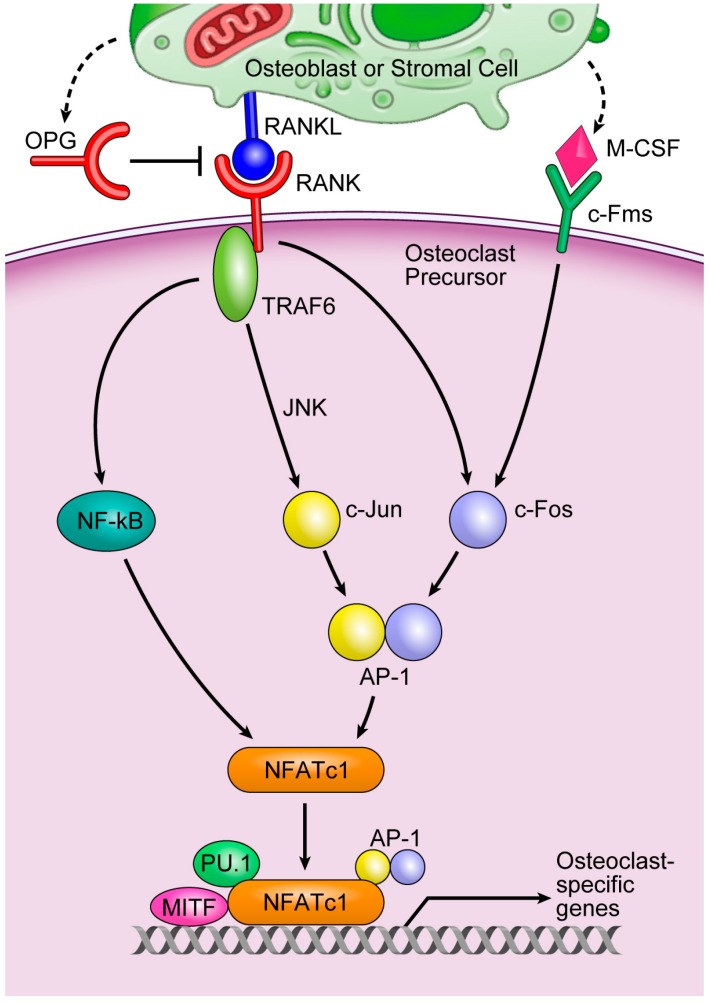
Figure 2.
A key osteoclastogenesis signaling cascade. Cited from [2]. The binding of M-CSF to its receptor, c-Fms, induces the transcription factor c-Fos, whereas the binding of RANKL to its receptor, RANK, leads to the recruitment of TNF-receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), the main adapter molecule of RANK. TRAF6 activates nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated kinases including c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). JNK activates the transcription factor c-Jun. RANKL/RANK also induces c-Fos to form AP-1, a heterodimeric transcription factor, with c-Jun. AP-1 and NF-κB then induce NFATc1, a master transcription factor that regulates osteoclast differentiation. NFATc1 works with other transcription factors, such as AP-1, PU.1, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) to induce various osteoclast-specific genes.