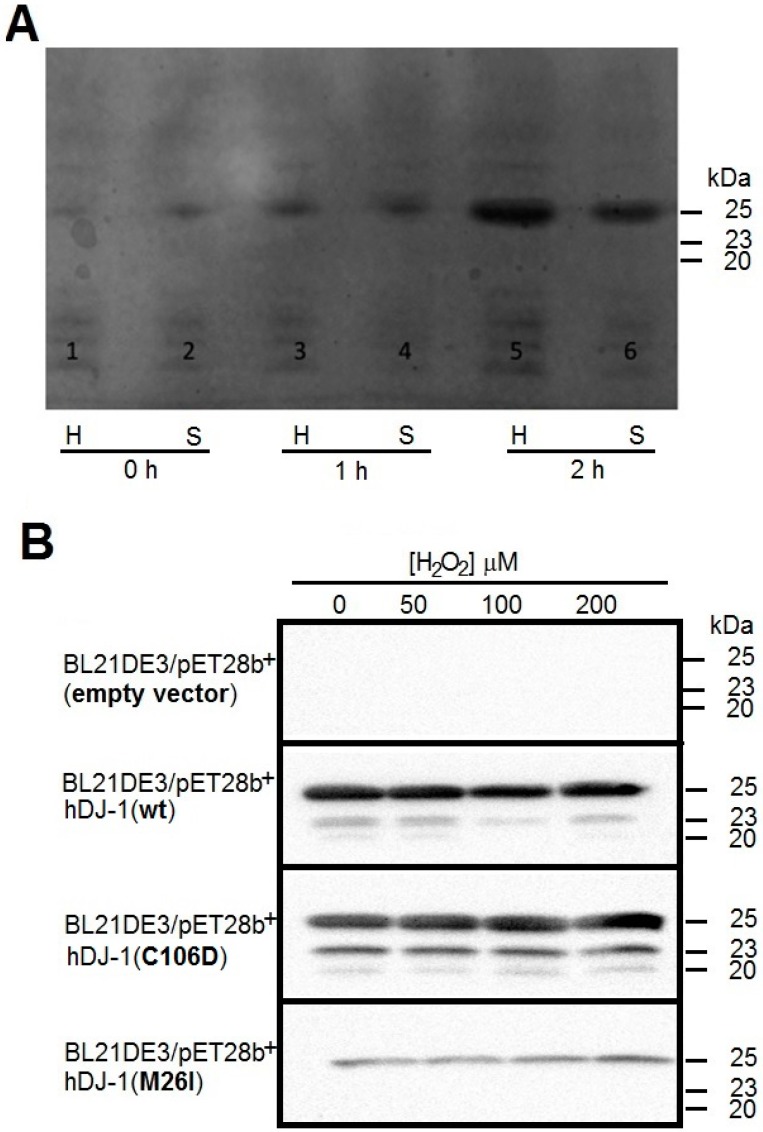
Figure 1.
Purification and proteolytic processing of exogenous hDJ-1 from Escherichia coli. (A) Coomassie staining of protein in crude homogenates and soluble fractions derived from E. coli transformed with human DJ-1 (BL21DE3/hDJ-1) and incubated with 100 µM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for 0, 1, and 2 h. Cell lysates were loaded (100 μg protein) and separated in 15% acrylamide/bis-acrylamide by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). H: crude homogenate, S: soluble fraction derived from the crude homogenate; (B) Western blot of lysates from untransformed (BL21DE3) or transformed bacteria with either a wild-type (wt, BL21DE3/hDJ-1), a PD associated mutant of DJ-1 (BL21DE3/hDJ-1 M26I) or a mutant of DJ-1 that mimic oxidized cysteine-SO2H (BL21DE3/hDJ-1 C106D) at the indicated concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Supernatants from lysed bacteria were purified by using a Ni2+-Sepharose HiTrap™ high performance (HP) column, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with rabbit polyclonal antiDJ-1 antibody 1:10,000 (anti-PARK7/DJ-1 antibody [EP2815Y]). Molecular weights are indicated on the right of the image in kDa.