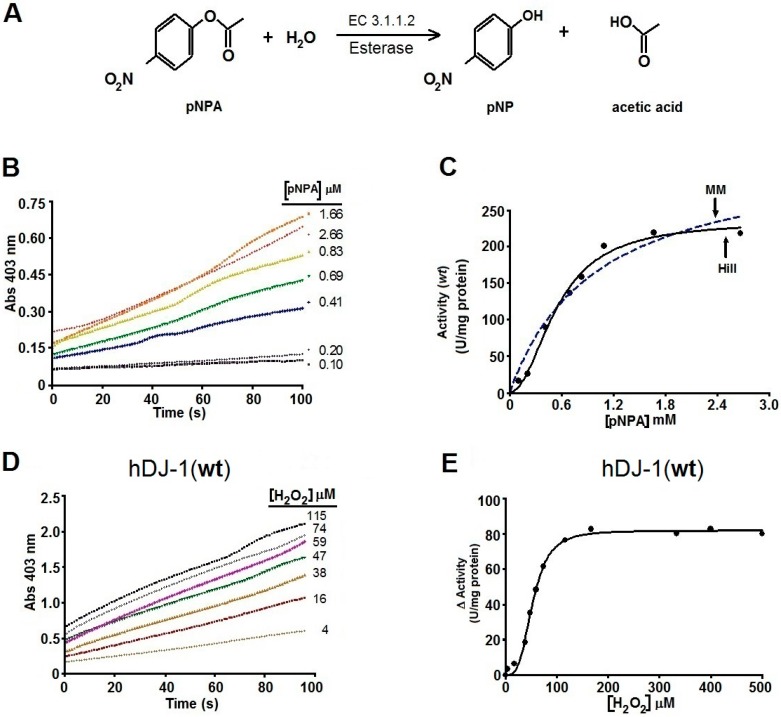
Figure 2.
hDJ-1 contains intrinsic esterase activity that is enhanced by exposure to reactive oxygen species (ROS). (A) Schematic showing the hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate (pNPA) by esterase to 4-nitrophenol (pNP) and acetate (EC 3.1.1.2); (B) Representative enzymatic kinetic time course for hDJ-1 esterase activity as spectrophotometrically monitored by the appearance of pNP at optical density (OD) of 403 nm at the indicated substrate concentrations (µM). To obtain specific esterase activity associated with hDJ-1, the absorbance values from control reactions that lacked hDJ-1 but contained H2O2, were subtracted from the values derived from the reactions containing hDJ-1 and H2O2. The enzymatic kinetic assay shown is representative of three experiments with similar results; (C) Representative enzymatic kinetic activity curve of hDJ-1(wt) (U/mg protein) based on the initial velocities (V0) obtained from the data shown in B, demonstrates a better sigmoidal fit for hDJ-1(wt) based on the Hill kinetic model (solid line, Equation (1) in methods) than a Michaelis–Menten fit (dashed line, Equation (2) in methods). Vmax = 235.10 ± 12.00 µmol of pNPA hydrolyzed/min/mg protein; S0.5 = 0.55 ± 0.040 mM; Hill coefficient (h) = 2.05 ± 0.28; (D) Representative enzyme kinetic trends of the esterase activity of recombinant hDJ-1, pretreated with the indicated increasing concentrations of H2O2, were obtained by spectrophotometrically monitoring the appearance of pNP at 403 nm at the indicated H2O2 concentrations; (E) Representative enzymatic kinetic of the change (∆) activity of hDJ-1(wt) (U/mg protein) based on the initial velocities (ΔActivity = [V0 with peroxide − V0 without peroxide]) obtained from the data shown in (D), shows that pretreating hDJ-1 with increasing concentrations of H2O2 (>10 µm) enhances its esterase activity and plateaus at a concentration of 100 µM.