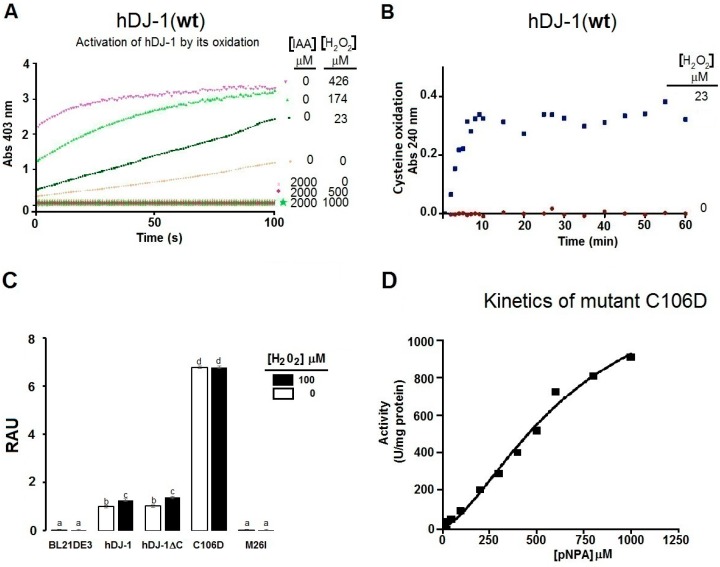
Figure 3.
Esterase of hDJ-1 requires the oxidation of C106. (A) Representative enzyme kinetic trends of the esterase activity of hDJ-1, in the presence or absence of the thiol (SH)-protecting chemical iodoacetamide (IAA), co-treated with increasing concentrations of H2O2; (B) Oxidation of the SH group by H2O2 as induced by exposing hDJ-1 to H2O2 led to the appearance of sulfonate that was monitored at OD 240 nm; (C) Esterase activity expressed as relative activity units (RAU). Data are means ± standard error in untransformed bacteria (BL21DE3), purified hDJ-1(wt), oxidant-mimetic mutant of hDJ-1 (hDJ-1∆C), hDJ-1(C106D), or the PD-associated mutant of DJ-1hDJ-1(M26I) at a saturating concentration of pNPA (2 mM). Note that hDJ-1(C106D) shows enhanced esterase activity towards pNPA compared to hDJ-1(wt), whereas hDJ-1(M26I) lacks esterase activity. Multiple comparison was done by performing a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA, p < 0.05) followed by post-hoc analysis, Tukey´s test. Lowercases indicates groups with statistically significant differences at p < 0.05; (D) Representative enzymatic kinetic curve of the oxido-mimetic mutant of hDJ-1(C106D) based on the initial velocities (V0) obtained from the data shown in (C), the kinetic parameters were: S0.5 = 676.40 ± 0.15 μM; h = 1.59 ± 0.15; Vmax = 1434 ± 183 U/mg protein.