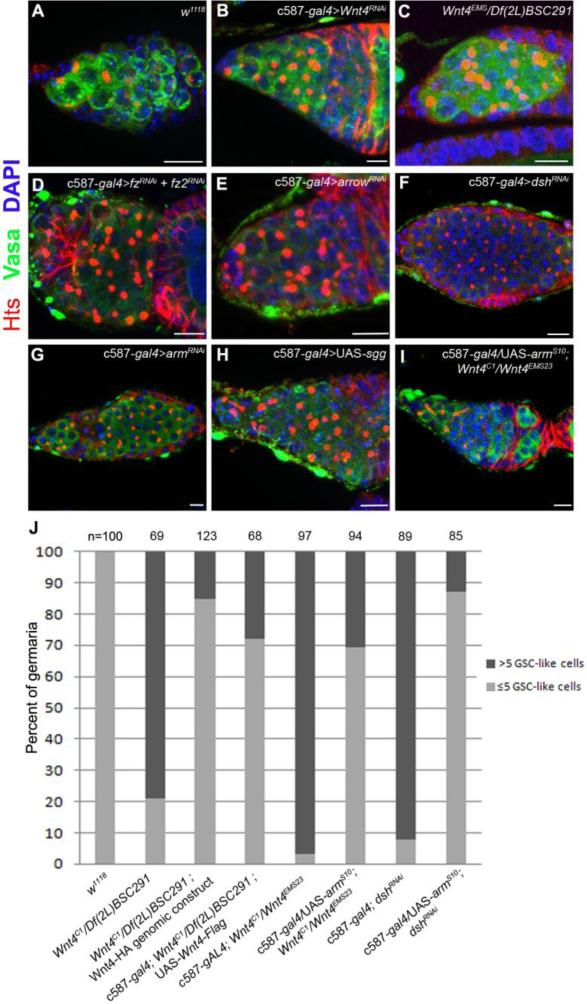
Fig. 1. Disruption of Wnt4 and canonical Wnt pathway components in escort cells results in the formation of GSC-like tumors.
(A-I) Germaria stained for Vasa (green), Hts (red) and DNA (blue). (A) Control germaria contain two to three GSCs. (B) Germaria from c587-gal4/+; UAS-Wnt4RNAi/+ and from Wnt4EMS/Df(2L)BSC291 displayed an increase of GSC-like cells with round fusomes. RNAi knockdown of (D) the fz and fz2 receptors, (E) the co-receptor arrow, (F) dsh or (G) arm, using the escort cell/early follicle cell c587-gal4 driver, results in the accumulation of GSC-like cells. (H) Over-expression of sgg in escort cells and early follicle cells also results in an expansion of undifferentiated germ cells. (I) Overexpression of a constitutively activated form of arm (armS10) suppresses the Wnt4C1/ Wnt4EMS23 phenotype. (J) A graph illustrating the percentage of germaria (Y-axis) that contained more (black bars) or less (light gray) than 5 round fusomes per germarium in the indicated genetic backgrounds (X axis). Note that the GSC-like tumor phenotypes observed after disruption of the canonical pathway are rescued by a genomic Wnt4 HA-tagged construct, as well as by expression of a Wnt4 cDNA or by expression of armS10 driven by c587-gal4. (Scale bars, 10 μm)