Figure 5.
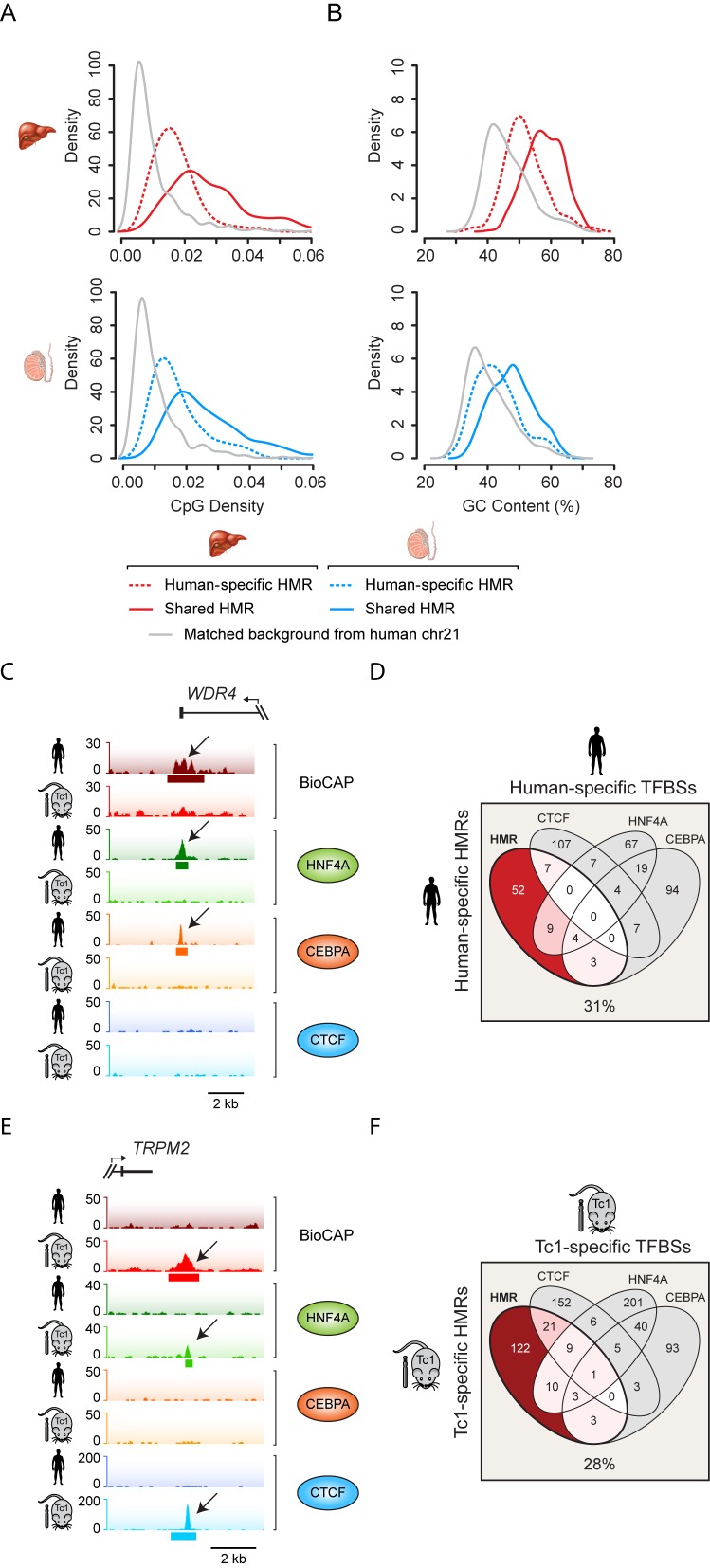
Species-specific transcription factor binding is widely associated with species-specific HMR formation. (A and B) CpG density (A) and GC content (B) plots of liver (upper panel, red) and testis (lower panel, blue) HMRs that are shared between human and Tc1 mouse (dark line) or are human-specific (dashed line). A background control is indicated (grey). (C) A snapshot illustrating a human-specific HMR corresponding to a human-specific transcription factor binding event as indicated by CEBPA and HNF4A ChIP-seq signal. (D) A 4-way Venn diagram comparing human-specific HMRs to human-specific transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) for CEBPA, HNF4A and CTCF on human chromosome 21. 31% of human-specific HMRs overlapped a human-specific TFBS. (E) A snapshot illustrating a Tc1 mouse-specific HMR corresponding to a Tc1 mouse-specific transcription factor binding event as indicated by HNF4A and CTCF ChIP-seq signal. (F) A 4-way Venn diagram comparing Tc1-specific HMRs to Tc1-specific transcription factor binding sites for CEBPA, HNF4A and CTCF on human chromosome 21. 28% of Tc1-specific HMRs overlapped a Tc1-specific TFBS.