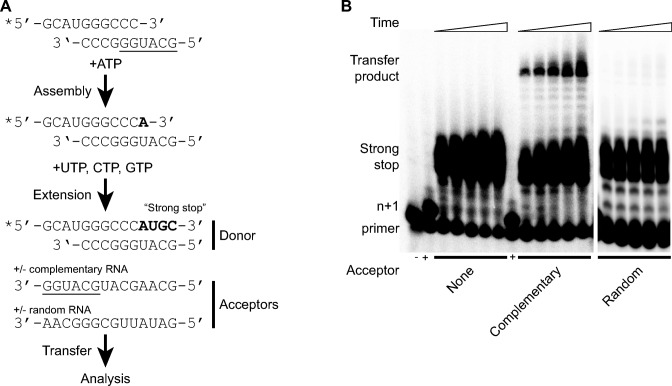
Figure 4.
A biochemically-defined in vitro recombination assay. (A) Scheme for in vitro template-switching assay. A radiolabelled (end labelled, indicated *) primer substrate pair known as sym/sub is the basis for the assembly of an elongation complex by the addition of ATP and purified polymerase protein. Addition of remaining nucleotides allows complete extension of the sym/sub template to form a strong stop product. The latter is considered the donor template to which acceptor template ribo-oligonucleotides are added. The complementary acceptor has six nucleotides (underlined) that have the potential to pair with the 3′ end of the extended sym/sub donor product. An alternative acceptor template with no complementarity was also tested. The products of the assay are analysed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). (B) Denaturing PAGE of in vitro reactions quenched at 5, 10, 20, 40 and 60 min after addition of the UTP/CTP/GTP and acceptor template (indicated below) mix. Reactions conducted in the absence (-) or presence (+) of ATP only indicated. The n + 1 product is the assembled elongation complex. The strong stop product is the fully extended sym/sub template. The high molecular weight products result from a template switch to the indicated RNA acceptor.