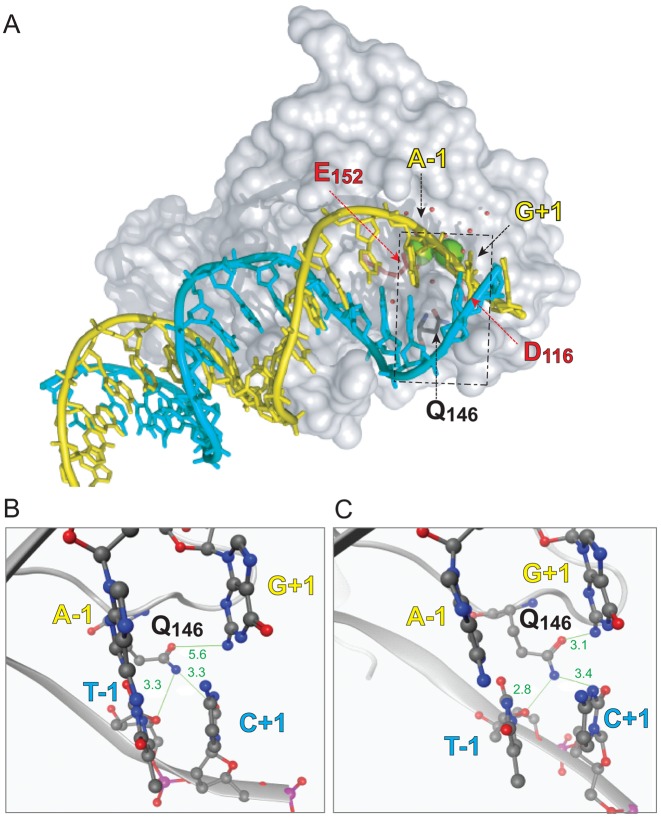
Figure 4.
Molecular model of the interaction of the HIV IN monomer with viral DNA. (A) Overall shape of an IN monomer interacting with the double-stranded DNA corresponding to the full-length viral DNA after reverse transcription and prior to ST (substrate for 3′-P). The catalytic core of IN is represented as gray surface. The catalytic amino acid triad DDE is colored as red sticks. Residue Q146 is colored as gray sticks. The two catalytic Mg2+ are shown as green spheres and the water molecules are presented as red balls. The viral DNA is shown with a ribbon backbone, with the bases shown as sticks. The strand cleaved during 3′-P is colored in yellow and its complementary strand in cyan. The dashed rectangle corresponds to the region highlighted in the close-up views of the active site of WT IN (B) and of the SH mutant (C). The DNA backbones are represented as ribbon with the −1 and +1 bases shown as sticks and balls colored according to their constituent elements. IN is represented as gray cartoon with residue Q146 shown as gray sticks and balls. Interatomic distances (in Å) between the Q146 side chain amine and oxy-substituent and the surrounding nucleobases are shown in green.