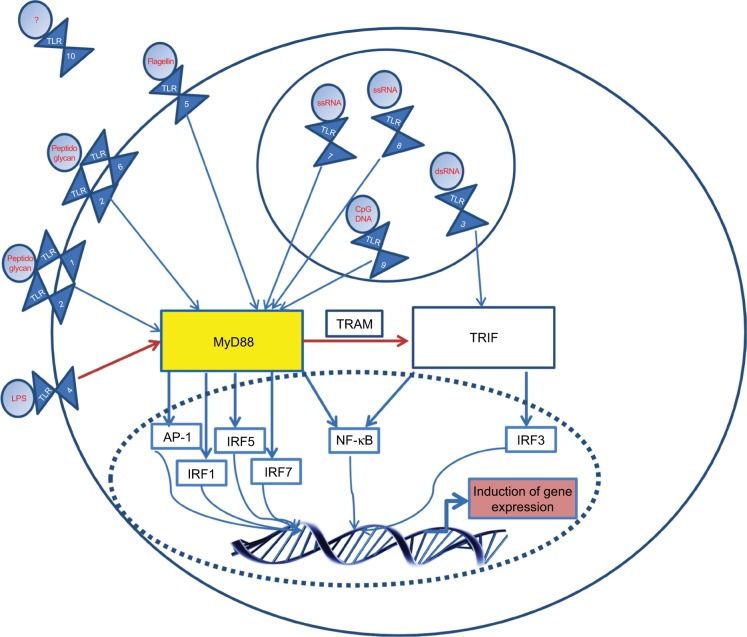
Figure 1.
Basic signaling of TLRs: upon ligation with their associated ligands (common ones are shown in red), TLRs form homo- or heterodimers.
Notes: Following ligation, TIR domains engage with adaptor proteins. TLRs 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 signal via the TIR domain-containing adaptor protein MyD88, while TLR3 uses the TRIF. TLR4 can move from the plasma membrane in order to switch signaling from MyD88 to TRIF, with the use of TRAM. A complex cascade, involving molecules such as IRAK-1, results in the induction of key transcription factors such as NF-κB. ‘’?”, unknown.
Abbreviations: dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; IFNβ, interferon-β; IL, interleukin; IRAK-1, IL-1R-associated kinases; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; TIR, toll IL-1 resistance; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; TLR, toll-like receptor; TRAM, TRIF-related adapt molecule; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adaptor protein-inducing IFNβ.