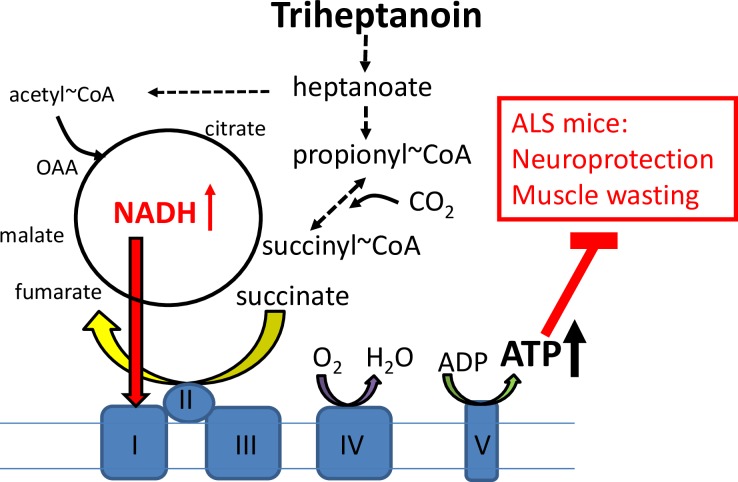
Fig 9. Hypothesized mechanisms of triheptanoin.
Triheptanoin is the triglyceride of heptanoate, which is metabolized to acetyl-CoA as well as propionyl-CoA providing alternative and anaplerotic fuel. Following carboxylation propionyl-CoA produces succinyl-CoA (anaplerosis), which via metabolism to oxaloacetate can increase ATP production and aid in further acetyl-CoA oxidation. Thus triheptanoin can improve mitochondrial energy production and thereby protect neurons and muscle against degeneration.