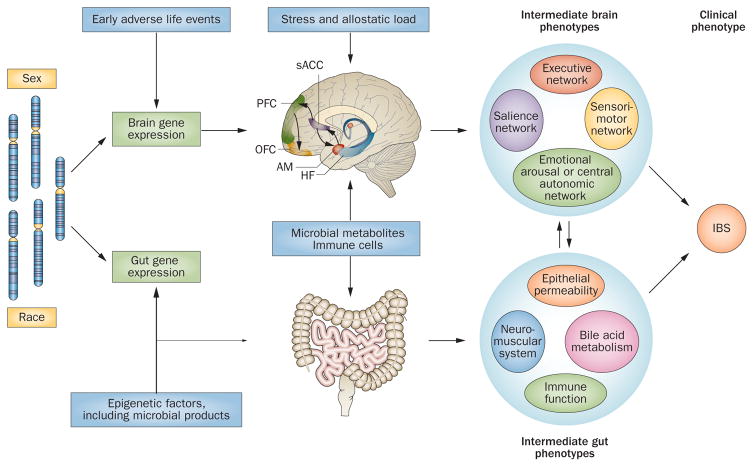
Figure 4.
Longitudinal brain–gut model of IBS pathophysiology. The interaction between genetic and epigenetic influences result in central and peripheral gene expression profiles that underlie the shaping of brain-based and gut-based intermediate phenotypes. Epigenetic factors provide the input from environmental influences on the development of intermediate phenotypes. Brain and gut intermediate phenotypes interact bidirectionally to shape the clinical phenotype of IBS. Abbreviations: AM, amygdala; HF, hippocampal formation; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; PFC, prefrontal cortex; sACC, subgenual anterior cingulate cortex.