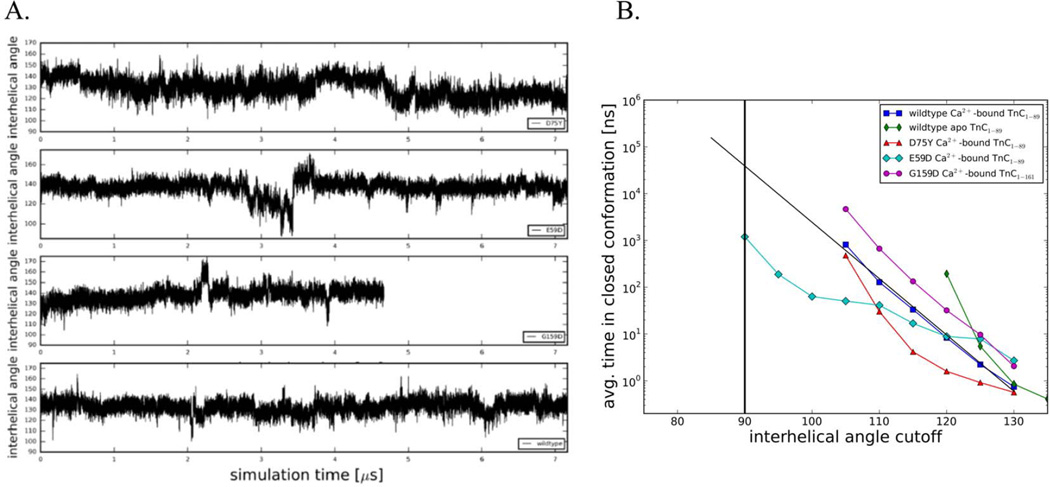
Figure 4.
(A) Interhelical angles over the course of the simulations for Ca2+-bound wildtype NcTnC, Ca2+-bound NcTnC-D75Y, Ca2+-bound NcTnC-E59D, and Ca2+-bound cTnC-G159D. Interhelical angles are a measure of the openness of the hydrophobic patch between cTnC helices A and B. An interhelical angle of ~135° corresponds to a closed conformation, while an angle of ~90° corresponds to a fully open conformation. (B) Average simulation time between opening events in dependence on the cutoff angle. Values for the Anton wild-type Ca2+-bound TnC simulation, the Anton wild-type apo TnC simulation (both from 17), and the three Ca2+-bound DMC mutation (NcTnC-D75Y, NcTnC-E59D, cTnC-G159D) simulations are shown. The widely accepted open-close cutoff criterion of 90° is marked by a vertical black line.