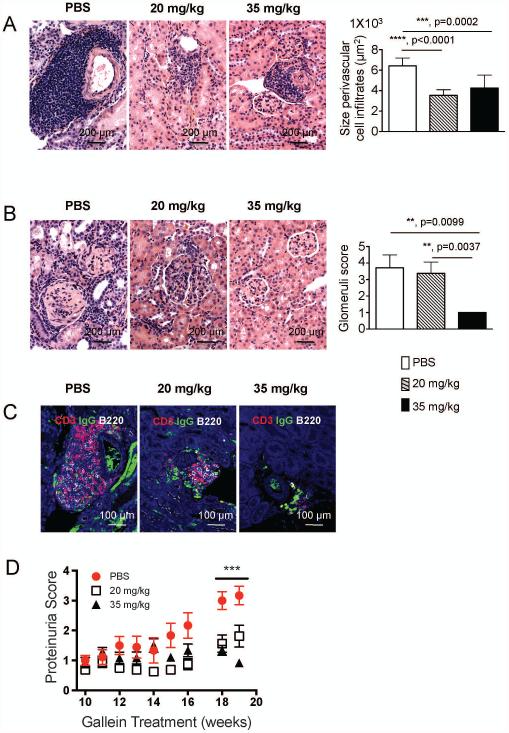
Figure 4. Inhibition of G protein βγ signaling prevents accumulation of immune cells in inflamed kidneys at early stages of experimental lupus.
After 20 weeks of gallein administration kidneys were fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin. A) 5 μm kidney sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Representative 200 x magnification pictures from kidneys showing inflammatory cell infiltrates around blood vessels are shown. Gross histological findings were confirmed by measurement of all perivascular cell infiltrates (right panel, n=8 mice/group). B) 5 μm kidney sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Representative 200 x magnification pictures from kidneys showing glomerular inflammation are shown. Right panel shows quantitative blinded evaluation of glomerular inflammation by a certified pathologist (right graph) in individual kidney sections (n = 8 kidney sections/group). C) Effects of gallein treatment on accumulation of CD3+ and B220+ cells around blood vessels in the kidneys of lupus prone mice. 5 μm kidney sections were stained with primary antibodies against CD3 (red), IgG (green) and B220 (white). Representative 200 x magnification pictures from two independent experiments with similar results are shown. D) Protein levels in the urine of mice were monitored. n=8 mice/group Data is expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical significance was calculated by non-parametric Mann Whitney test. **, p=<0.005, ***, p<0.0005, ****, p<0.0001.