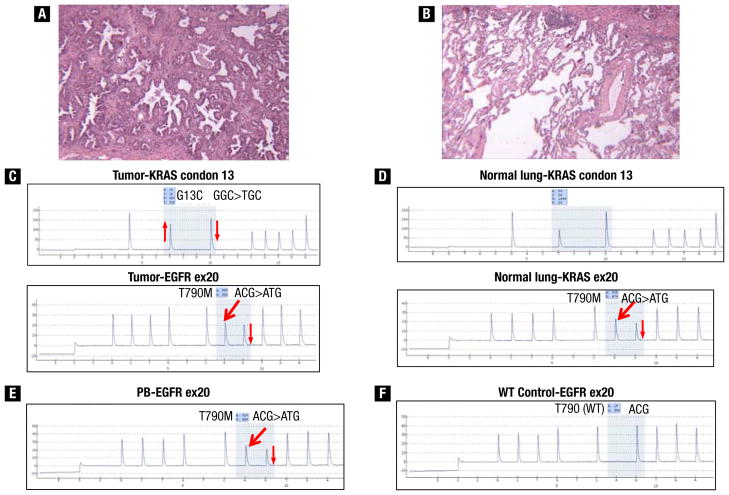
Figure 1.
(A and B) Histopathologic sections (patient 1) showing moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma with bronchoalveolar differentiation and microdissected normal lung. (C) Pyrograms from adenocarcinoma showing KRAS G13C mutation and EGFR exon 20 T790M mutation. (D) Pyrograms from adjacent normal lung sample showing wild-type KRAS sequence and EGFR exon 20 T790M mutation, indicating that the KRAS mutation is somatic, whereas the EGFR T790M mutation is occurring in the germline. (E) Pyrogram from peripheral blood showing the EGFR exon 20 T790M mutation, confirming its germline origin. (F) Pyrogram from a placental control demonstrating the wild-type (WT) T790 sequence for comparison with the mutant sequences present. The thick red arrows indicate new signals in the pyrograms caused by the presence of the mutant allele, and the thin red arrows indicate relative changes (up or down) in signals in the pyrograms caused by the presence of mutant alleles.
Abbreviations: ex = exon; PB = peripheral blood.