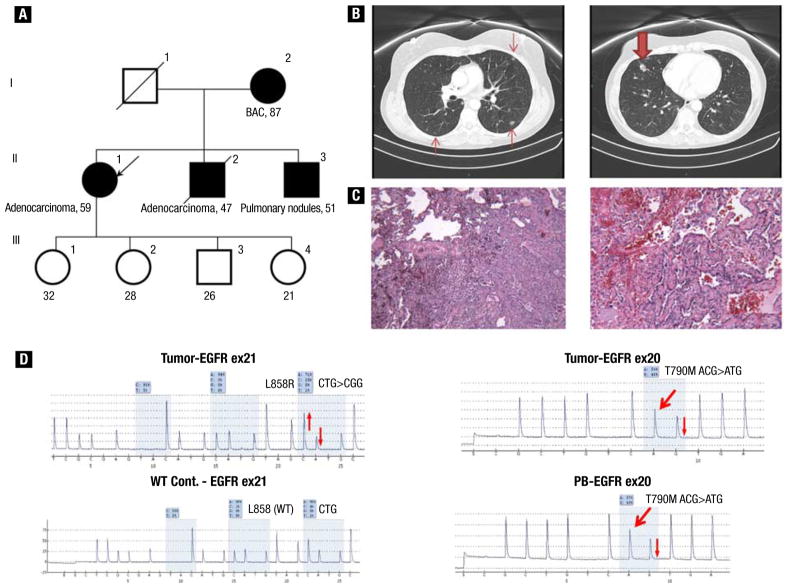
Figure 2.
(A) Pedigree of family (case 2) with multiple cases of lung adenocarcinoma. (B) Computed tomographic scan of chest at diagnosis, which showed right middle lobe nodule measuring 1.6 cm (bold arrow) and bilateral ground-glass opacities (arrows). (C) Pathologic examination showed predominantly acinar moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, with focal papillary and bronchoalveolar patterns. (D) Pyrograms showing somatic EGFR exon 21 L858R mutation, wild-type EGFR exon 21 L858 control (WT Cont.) for comparison, and EGFR T790M mutations present in tumor and peripheral blood (PB), indicating its germline origin. The thick red arrows indicate new signals in the pyrograms caused by the presence of the mutant allele, whereas the thin red arrows indicate relative changes (up or down) in signals in the pyrograms caused by the presence of mutant alleles.