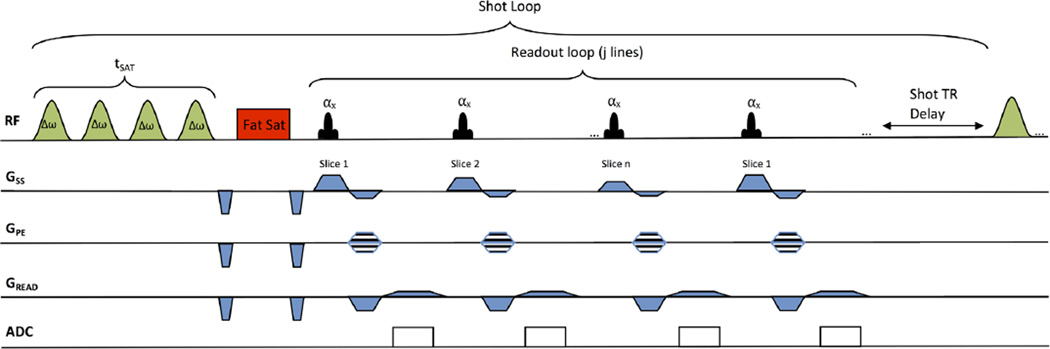
FIG. 1.
Pulse sequence diagram for a multislice, CEST-prepared sequence. CEST magnetization preparation involves a frequency-selective saturation pulse consisting of a train of Hanning windowed rectangular pulses with short interpulse delays. This is followed by a chemical shift selective fat saturation pulse and a segmented radiofrequency spoiled gradient recalled readout (SPGR) acquisition with centric phase and interleaved slice-encoding order. The readout acquisition acquires a single line of k-space from each slice before repeating a different k-space line for the same slice again. Multiple partitions (magnetization preparations/multislice readout) could be used to segment k-space across multiple CEST magnetization preparations. The number of k-space lines (j) acquired for each magnetization preparation is equal to the number of phase encodes multiplied by the number of slices (n) and divided by the number of partitions. Following saturation and acquisition of SPGR segments, a delay is added to allow for T1 recovery.