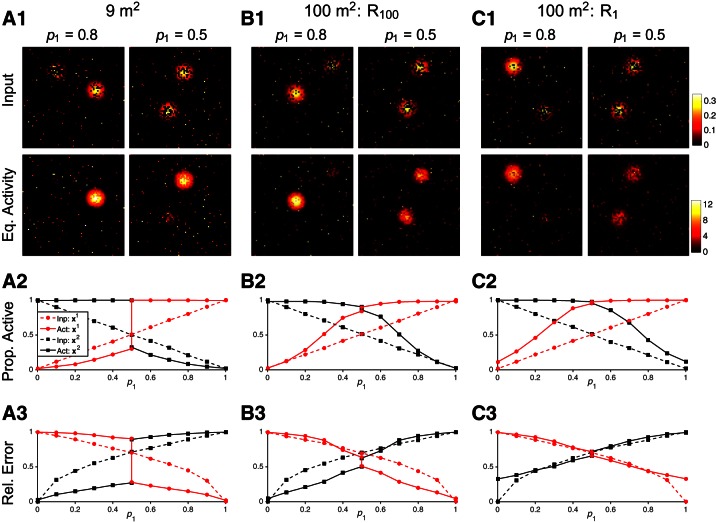
Fig. 12.
Pattern completion and pattern separation in large square environments. For each trial, a proportion (p1) of place cells are driven by the external input I(x1; 0.3) and the remaining cells are driven by I(x2; 0.3) (Eq. 8). Given these competing, incomplete inputs, the megamap performs pattern completion over at least 1 of the 2 locations regardless of the operational mode. A: the megamap representing 9 m2 operates in the WTA mode. A1: when 80% of place cells receive input for x1, a single equilibrium activity (Eq. activity) bump fully represents x1 (left). When exactly half of the place cells receive input for each location, the megamap still fully represents one location (right). A2: when p1 > 0.5, pattern completion is apparent in that all place cells representing x1 are active in the equilibrium activity bump (solid red), even though only a fraction of these cells receive input (dashed red). The activity bump over x2 is suppressed, because only a fraction of place cells receiving input for x2 are active (black). The opposite is true when p1 < 0.5. When p1 = 0.5, the activity bump represents either x1 or x2, but never both. A3: when p1 > 0.5, the error in place cell activity encoding x1 (solid red) is less than the error in the inputs (dashed red), a characteristic of pattern completion. When p1 < 0.5, the error in place cell activity is greater than the error in the inputs, a characteristic of pattern separation. B and C: the megamap representing 100 m2 operates in the combinatorial mode. B: when x1 and x2 are both in the last subregion learned (R100), the megamap performs pattern completion over both locations when 0.2 ≤ p1 ≤ 0.8, because more place cells representing each location are active than receive input. Both locations are strongly represented through 2 co-active equilibrium activity bumps when 0.4 ≤ p1 ≤ 0.6, because the error in place cell activity is less than the error in the inputs at both locations. Pattern separation is not as apparent as in the WTA mode since the weaker activity bump closely follows the external input. C: when x1 and x2 are both in the first subregion learned (R1), the representation of any location is weaker. Although the megamap still performs pattern completion at all locations, the error in place cell activity closely follows the error in the input. Prop. active, proportion of active cells; Rel. error, relative error.