Figure 5.
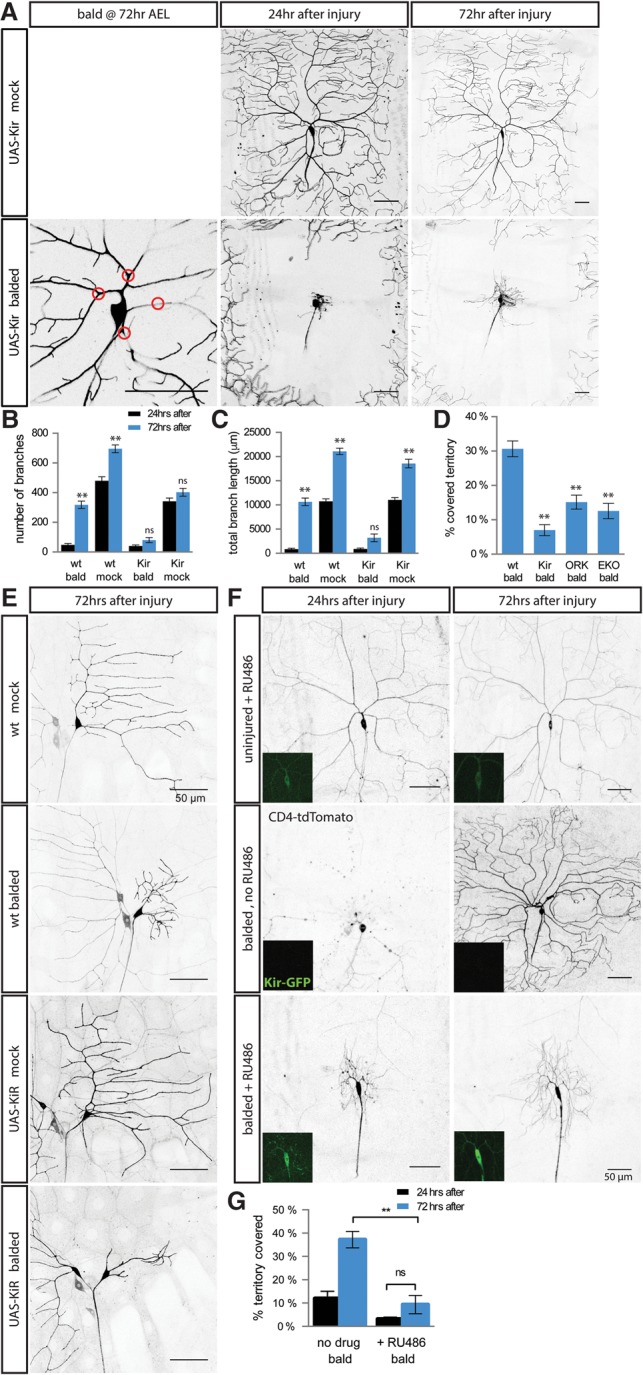
Manipulating electrical activity blocks injury-induced dendrite growth. (A) Class IV neurons expressing Kir2.1 have relatively normal dendrite outgrowth in the absence of injury (top row) but a dramatically reduced growth after balding (bottom row). Red circles indicate points where dendrites will be severed. (B,C) Compared with wild-type neurons and uninjured Kir2.1-expressing neurons, Kir2.1-expressing class IV neurons have dramatically less branch formation (B) and dendrite extension (C) between 24 h (black) and 72 h (blue) after balding. (**) P < 0.001 comparing 72 h with 24 h after balding or after mock injury by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. n = 14 balded wild-type neurons, 12 mock wild-type neurons, 17 balded Kir neurons, and 15 mock Kir neurons. (D) Electrically inactivating class IV neurons using K+ channel transgenes decreases territory recoverage after balding. (**) P < 0.0001 compared with wild type by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. n = 14 wild-type balded neurons, 17 Kir balded neurons, 20 ORK balded neurons, and 6 EKO balded neurons. (E) Kir expression decreases class I neuron dendrite regeneration after injury without affecting the development of uninjured neurons. n = 24 wild-type balded neurons, 36 wild-type mock neurons, 20 Kir balded neurons, and 31 Kir mock neurons. (F,G) Defects in injury-induced outgrowth are independent of early dendrite development. (Inset) Twenty-four hours before injury, flies with ppk-CD4-tdTomato ppk-GS, UAS-Kir2.1-GFP were given RU486 or no drug to induce Kir2.1-GFP expression. (G) While drug treatment without injury did not alter dendrite morphology, RU486-induced Kir2.1 significantly decreased territory recoverage after balding compared with balded neurons with no RU486. (ns) P > 0.05; (**) P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. n = 11 neurons without RU486 and 10 neurons with RU486. Bar, 50 μm.
