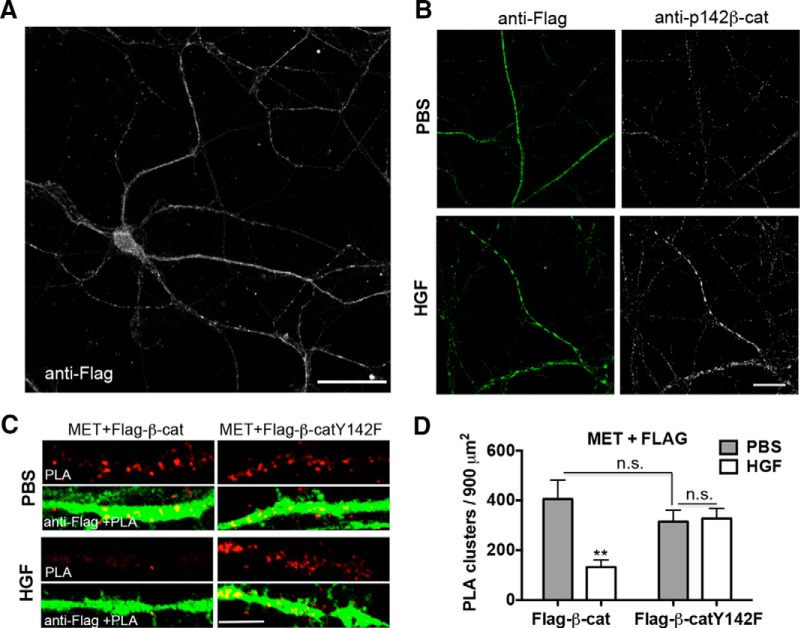
Figure 4.
HGF modulates MET/β-catenin complex via phosphorylation of β-catenin at Y142. A, Neurons were transfected with flag-tagged wild-type β-catenin (Flag-β-cat). Representative confocal microscopy image of transfected neuron with total flag immunoreactivity (white) was shown. Note that transfected β-catenin was distributed along the entire neuron and processes. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Representative confocal microscopy images of Flag-β-cat-transfected neurons with total flag (green) and p142- β-catenin immunoreactivity (white). Note the positive immunostaining of p142- β-catenin in the Flag-β-cat-transfected neuron with stimulation of HGF. Scale bar, 25 μm. C, Representative confocal microscopy images of PLA staining of MET and flag in primary cultures of neocortical neurons at 14 DIV following treatment with PBS or HGF for 10 min. Neurons were transfected with Flag-β-cat or β-cateninY142F (Flag-β-catY142F) at 5 DIV. Red fluorescent profiles represent regions of PLA signal amplification denoting MET and flag colocalization. For comparison, the total flag immunoreactivity (green fluorescence) in the same field is illustrated. Scale bar, 5 μm. D, Quantitative analysis of the MET/flag PLA signals. Error bars represent the SEM; N = 22 cells from three independent cultures in each group. Note that there is a decrease in PLA signal with HGF in the wild-type Flag-β-catY, but that there is no change with HGF in the Flag-β-catY142F condition. **p < 0.01 (HGF vs PBS in Flag-β-cat-transfected group); p = n.s. (Flag-β-cat vs Flag-β-catY142F with PBS stimulation, HGF vs PBS in Flag-β-catY142F-transfected group).