Figure 1.
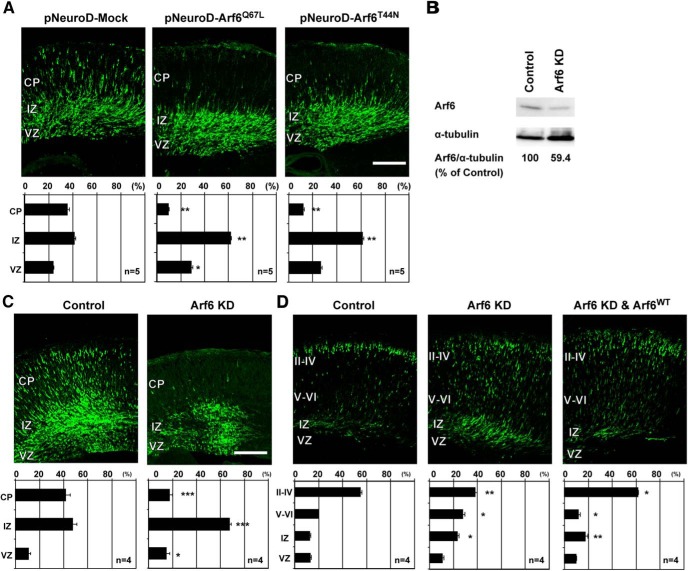
Arf6 is required for cortical neuronal migration. A, Representative micrographs of E17.5 cerebral cortices electroporated with the pNeuroD plasmids carrying Mock, Arf6Q67L, or Arf6T44N in combination with pCAGGS-EGFP at E14.5 (n = 5 embryos). B, Immunoblot analysis of cultured cortical neurons transfected with Arf6 shRNA (Arf6 KD) or its scramble shRNA (Control) for 3 d. The numbers indicate the percentage of endogenous Arf6 expression level relative to α-tubulin. C, Representative micrographs of E17.5 cerebral cortices electroporated with the pmU6pro plasmids carrying scramble sequence (Control) or Arf6 shRNA (Arf6 KD) in combination with pCAGGS-EGFP at E14.5 (n = 4 embryos). D, Representative micrographs of P0 cerebral cortices electroporated with Control, Arf6 KD, or Arf6 KD and Arf6WT plasmids in combination with pCAGGS-EGFP at E14.5 (n = 4 embryos). Bottom graphs in A, C, and D show the quantification of the distribution of EGFP-positive cells in cortical layers. Data were presented as mean ± SEM and statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer’s tests in A and D (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01), and by unpaired t test in C (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005). n in the graph indicates the number of embryos examined. Scale bars: A, C, D, 200 μm.