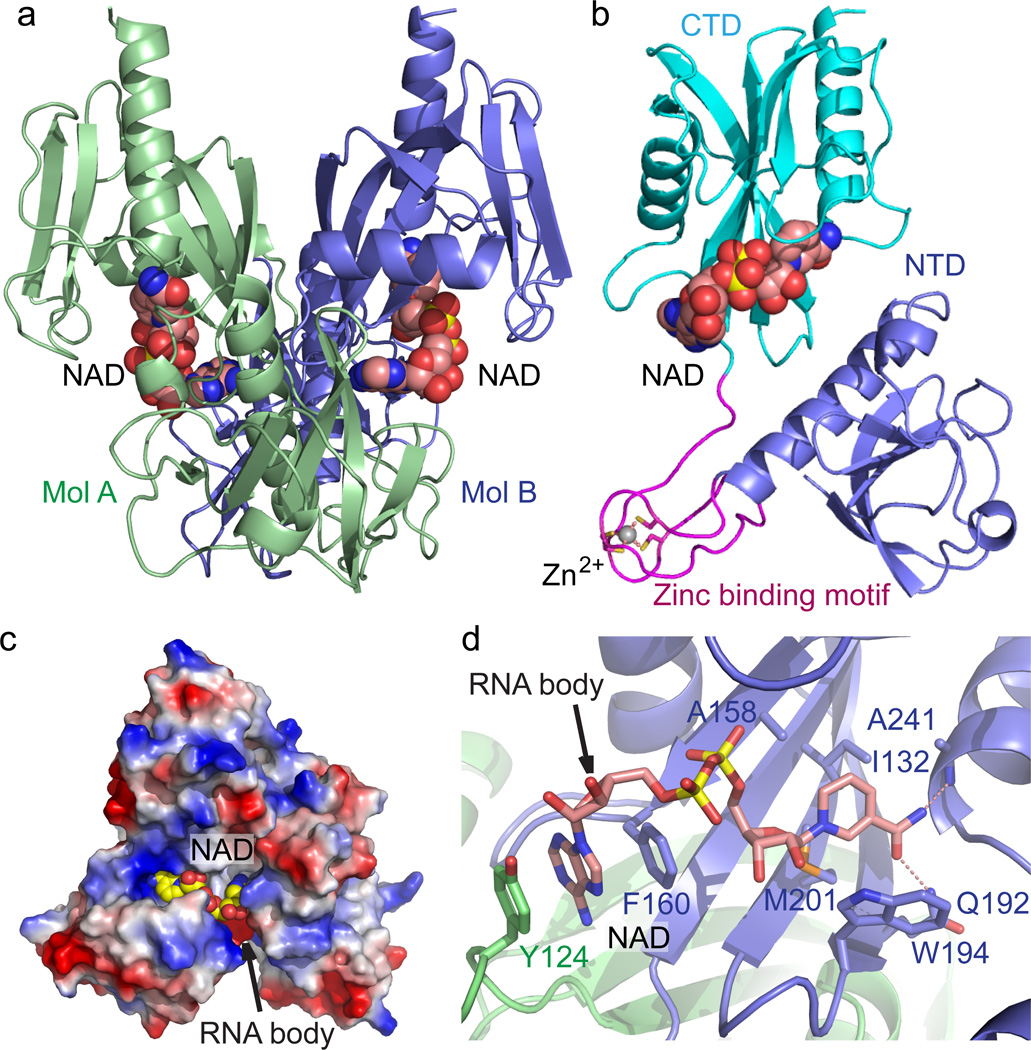
Figure 1. Crystal structure E. coli NudC in complex with bound NAD.
(a) Overall structure of the E. coli NudC dimer in complex with NAD. The two monomers of NudC (Mol A and Mol B) are colored in slate and light green, respectively. The bound NAD molecules are shown in space filling representation. (b) A detailed structural representation of a monomer of NudC-NAD complex. The NTD, zinc-binding motif, and CTD are colored in slate, magenta, and cyan, respectively. Zinc ion coordination is highlighted with dashed red lines. (c) An electrostatic surface view of the NAD binding pocket of NudC. The postulated NAD-RNA extension channel is highlighted with the arrow. In addition, a positively-charged surface patch locates at the entrance of the NAD binding pocket, suggesting a plausible role in RNA binding. (d) The specific recognition of NAD by NudC. The residues involved in NAD binding are shown in a stick representation. The hydrogen bonding interactions are shown as dashed red lines. The arrow indicates the postulated position of RNA body extension.