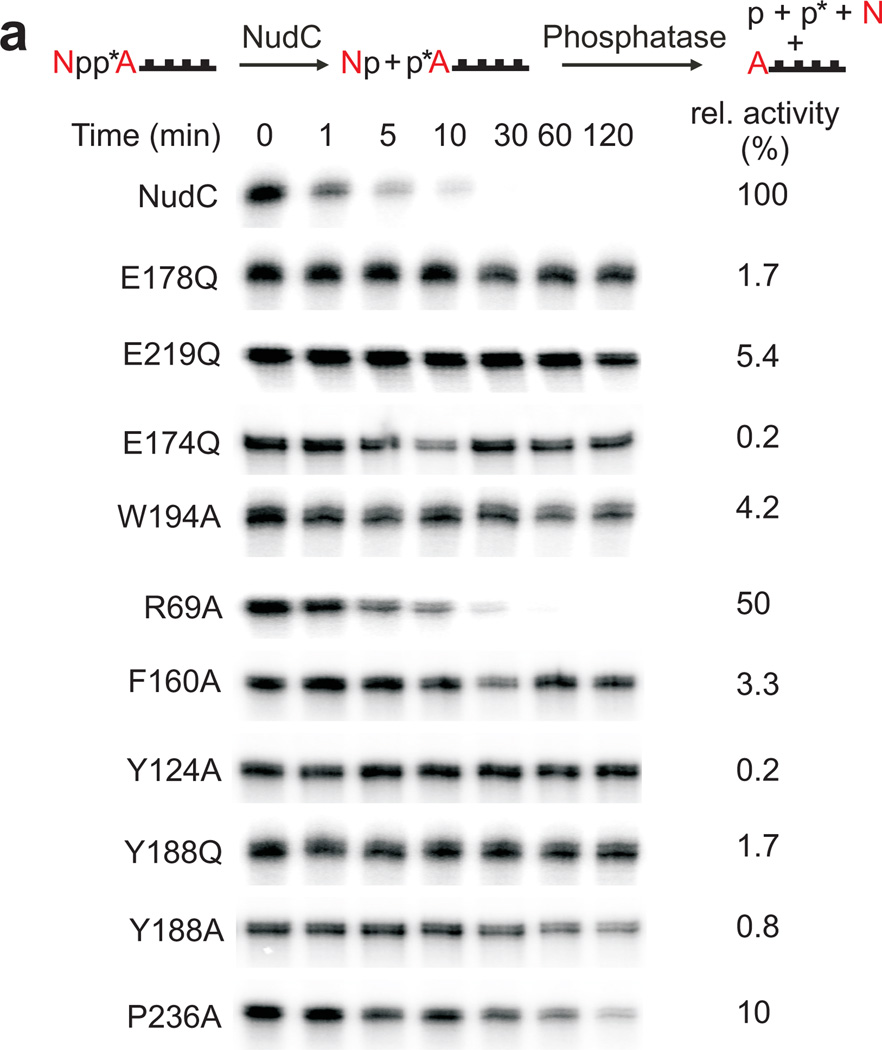
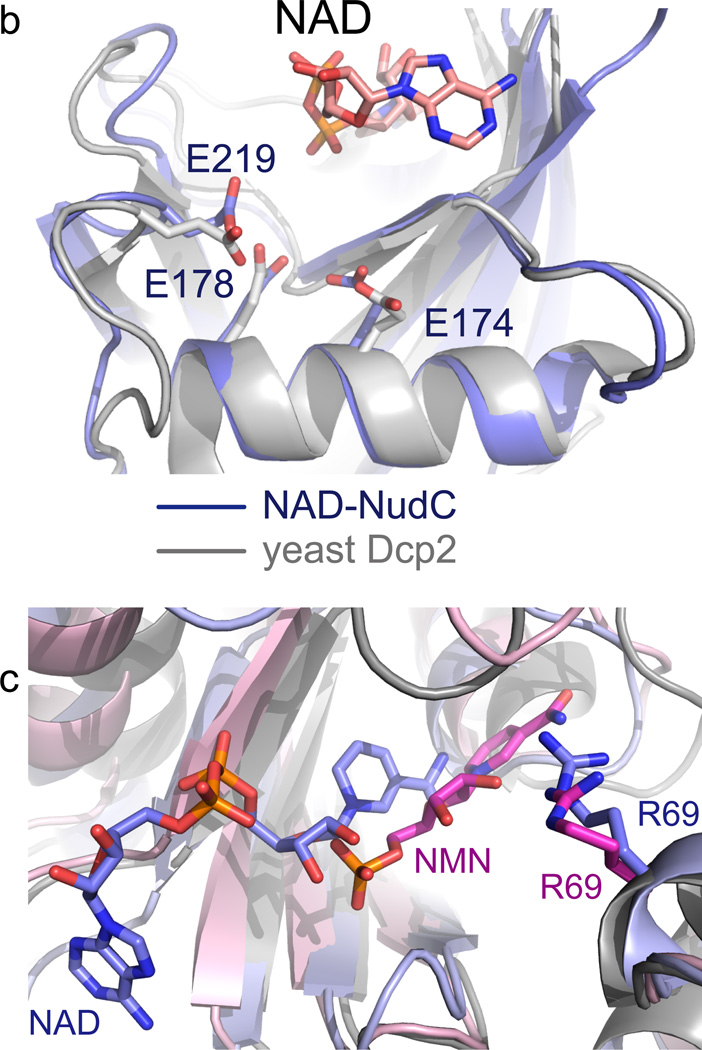
Figure 3. Mutagenesis of NudC.
(a) Decapping of full-length E. coli NAD-RNAI (NppA = NAD; N: nicotinamide riboside, pp: pyrophosphate, A: adenosine) by NudC and single-mutants. NAD-RNA contains a site-specific 32P label at the pyrophosphate bridge (asterisk) which becomes accessible to excess phosphatase only upon hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate4, causing disappearance of the radioactive RNAI band. Aliquots taken at the indicated time points are separated on denaturing PAGE gels. Experiment was carried out three times. Full denaturing PAGE gels are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8a. (b) The superposition of the Nudix motif of NudC and yeast Dcp2 showing the conserved glutamates. (c) Superposition of NudC-NAD (in light blue) and NudC-NMN (in pink), relative to Arg69.