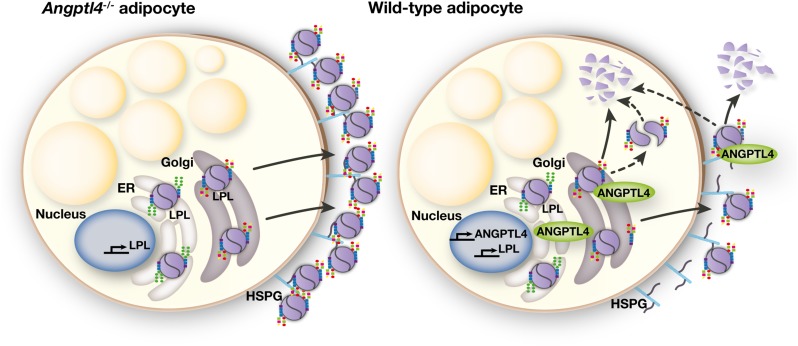
Fig. 11.
Schematic model. Within the ER, LPL acquires oligosaccharide side chains via cotranslational transfer of oligosaccharides high in mannose residues. Upon translocation to the Golgi apparatus, the high-mannose oligosaccharides are trimmed and replaced by more complex oligosaccharides. In the absence of ANGPTL4 (i.e., Angptl4−/− adipocytes), LPL with complex oligosaccharide side chains is packaged in secretory vesicles and secreted. Secreted LPL accumulates on the cell surface of adipocytes, mostly bound to HSPGs. In ANGPTL4-expressing adipocytes (i.e., wild-type adipocytes), ANGPTL4 interacts with LPL in a post-ER compartment. This interaction leads, potentially via converting LPL homodimers to monomers, to degradation of LPL. This results in a specific reduction of LPL with complex oligosaccharide side chains in wild-type adipocytes versus Angptl4−/− adipocytes. Once secreted, ANGPTL4 also reduces levels and activity of secreted LPL.