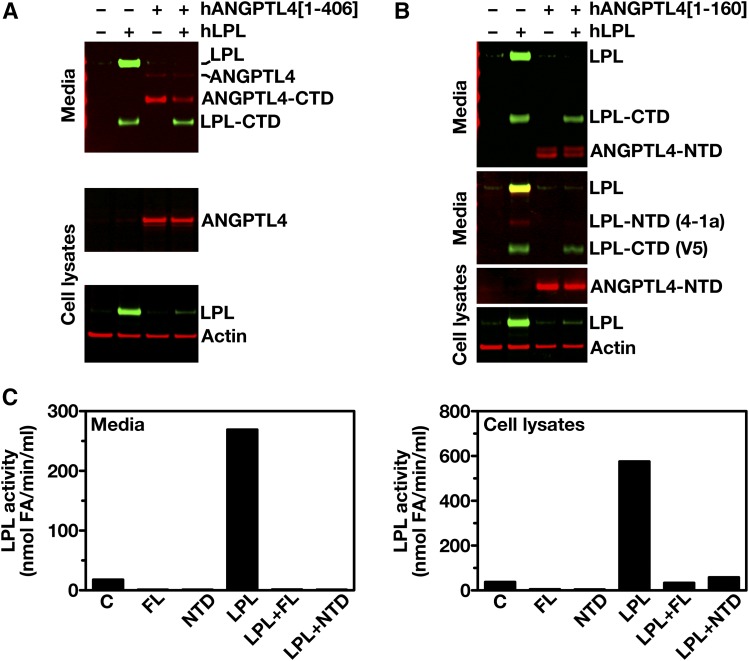
Fig. 2.
ANGPTL4 inactivates LPL inside cells. A: Western blots of cell culture media and cell lysates of CHO pgsA-745 cells that had been cotransfected with an expression vector for Flag-tagged hANGPTL4 (hANGPTL4[1–406]) and a vector for V5-tagged hLPL (or empty vector). Western blots were probed with an anti-Flag antibody to detect ANGPTL4 (red), an anti-V5 antibody to detect LPL (green), and an anti-actin antibody (red) (as a loading control). LPL-CTD, C-terminal domain of LPL; ANGPTL4-CTD, C-terminal domain of ANGPTL4. B: Western blots of cell culture media and cell lysates of CHO pgsA-745 cells cotransfected with an expression vector for myc-tagged hANGPTL4 (hANGPTL4[1–160]) and a vector for V5-tagged hLPL (or empty vector). Western blots were probed with an anti-Myc antibody to detect ANGPTL4 (red), an anti-V5 tag antibody (green), or Mab 4-1a (red) to detect LPL, and an anti-actin antibody (red) (as a loading control). LPL-CTD, C-terminal domain of LPL; LPL-NTD, N-terminal domain of LPL; ANGPTL4-NTD, N-terminal domain of ANGPTL4. C: LPL activity levels in the culture media and cell lysates of CHO pgsA-745 cells that had been transfected with an empty vector alone (C), full-length hANGPTL4 alone (FL), N-terminal domain of hANGPTL4 alone (NTD), full-length ANGPTL4 and LPL (LPL+FL), the N-terminal domain of ANGPTL4 and LPL (LPL+NTD).