Fig. 3.
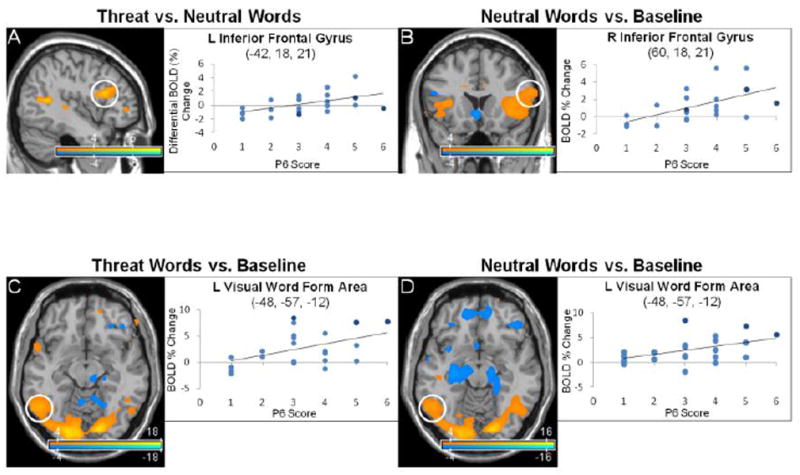
Anterior language network and visual word form area activations correlated to persecutory delusion severity in the emotional word paradigm. Statistical parametric maps show blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) neural activation changes thresholded at a voxelwise p-value of 0.001 for visualization purposes. (A) P6 scores (persecutory delusion severity) positively correlated with left inferior frontal gyrus, pars opercularis/triangularis (-42, 18, 21: peak z-score = 4.543, corrected p-value = 0.002) activations in the threat word vs. neutral word contrast. (B) P6 scores correlated positively with right (60, 18, 21: peak z-score = 5.934, corrected p-value < 0.001) and left (-48, 9, 9: peak z-score = 5.257, corrected p-value < 0.001; not shown) inferior frontal gyri for the neutral word vs. baseline contrast. (C-D) Visual word form area (-48, -57, -12) activations positively correlated with P6 scores in both the threat word (peak z-score > 8, corrected p-value < 0.001) and neutral word vs. baseline contrasts (peak z-score = 6.672, corrected p-value < 0.001). In the scatter plots, light blue indicates schizophrenia subjects, dark blue schizoaffective subjects.
