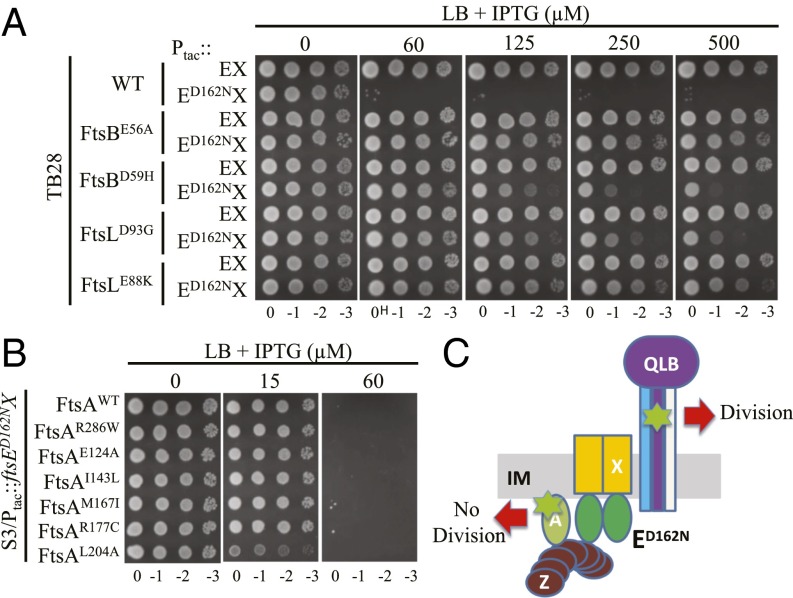
Fig. 4.
Hyperactive ftsB and ftsL mutations, but not hyperactive ftsA mutations, confer resistance to overexpressed FtsED162NX. (A) Hyperactive ftsB and ftsL mutations confer resistance to overexpressed FtsED162NX. Plasmid pSD221 and its variant pSD221-D162N were transformed into strains TB28, BL167 (TB28, ftsBE56A), BL140 (TB28, ftsBD59H), MT10 (TB28, ftsLE88K), and BL154 (TB28, ftsLD93G). A single transformant of each strain from LB + 0.2 M sucrose plates was then resuspended in 1 mL of LB medium and serially diluted. Three microliters of each aliquot was then spotted on the LB plates or the LB + 0.2 M sucrose plates with appropriate antibiotics and increasing concentrations of IPTG. The plates were incubated at 30 °C overnight before photography and only results from LB plates are shown. (B) Hyperactive ftsA mutations do not confer resistance to overexpressed FtsED162NX. Plasmid pSD221-D162N was transformed into strain S3 and its derivatives carrying hyperactive ftsA mutations. A spot test was performed as in A. (C) Diagram indicating the location of hyperactive mutations and the response to FtsED162NX. The hyperactive mutations are indicated by the green symbol and are in FtsA or FtsL/FtsB.