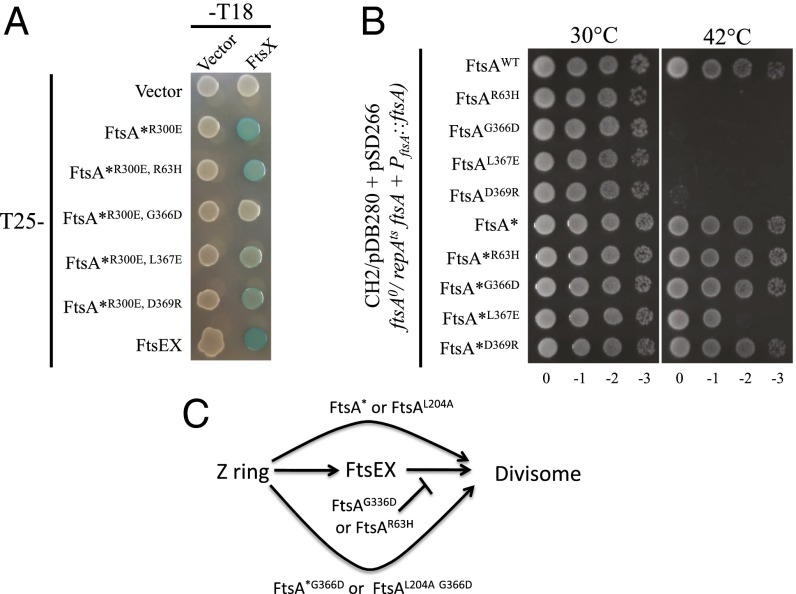
Fig. 7.
FtsED162NX resistant ftsA mutations impair the FtsA–FtsX interaction and inactivate FtsA function. (A) BTH assay to assess the interaction between FtsA mutants and FtsX. Pairs of plasmids harboring T25-FtsA*R300E (T25-FtsAR286W, R300E) and FtsX-T18 or their variants were cotransformed into BTH101. Single transformants of each combination were then resuspended in LB medium and 3 µL of each aliquot was spotted on LB plates containing appropriate antibiotics, 25 µM IPTG and 40 µg/mL X-gal. The plates were then incubated at 30 °C overnight before photography. (B) FtsA mutants impaired for interaction with FtsX cannot complement an FtsA-depletion strain and the ftsAR286W mutation suppresses this defect. Plasmid pSD266 (pACYC184, PftsA::ftsA) or its variants harboring different ftsA mutations were transformed into strain CH2/pDB280 (ftsA0 recA56 srlD::Tn10/pSC101ts, PftsA::ftsA). Single transformants of each strain obtained at 30 °C were then resuspended in LB medium and serially diluted. Three microliters of each aliquot was spotted on LB plates with appropriate antibiotics. The plates were then incubated at 30 °C and 42 °C overnight before photography. (C) Summary of the behavior of ftsA alleles in divisome assembly. ftsAG366D and ftsAR63H block divisome assembly; however, they are rescued by some ftsA mutations that bypass FtsEX. Note, some ftsA mutations that bypass FtsEX do not rescue and are considered weak, as explained in the text.