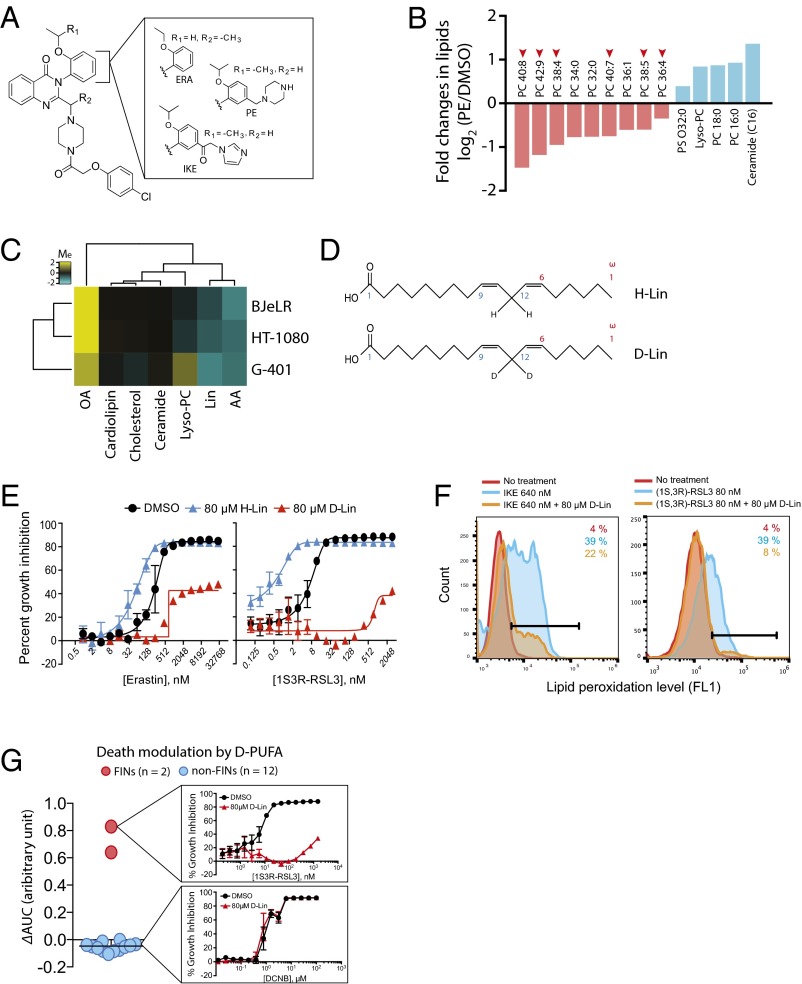
Fig. 2.
PUFAs play a functional role in ferroptotic cell death. (A) Structure of erastin analogs used in this study. ERA, erastin (3); IKE, imidazole ketoerastin (61); and PE, piperazine erastin (2). (B) Lipidomics analysis revealed loss of PUFAs is the most prominent change during ferroptosis. HT-1080 cells were treated with PE or vehicle (DMSO) and lipid metabolites were extracted as described in Methods. The amount of individual lipid metabolites in the sample was determined using an LC-MS instrument, and changes in the amount of lipid metabolites were calculated by dividing the amount in PE sample by that in DMSO sample. The graph shows the name of top changing lipid metabolites (nine down-regulated and five up-regulated) and the value of fold changes in log2 scale. The number of carbons and double bonds in sn-2 position fatty acids are indicated. For example, PC 40:8 indicates phosphatidyl choline (PC) that has a fatty acid of 40 carbon and 8 double bonds in sn-2 position. PS, phosphatidyl serine. (C) Modulation of ferroptosis sensitivity by different lipid species. PUFAs sensitized cells to ferroptosism, whereas OA prevented ferroptosis. Yellow indicates cell death suppression and blue represents cell death sensitization. Modulatory index (Me) was calculated as previously described (1). (D) Structures of natural LA (H-Lin) and deuterated LA (D-Lin). (E) Suppression of ferroptosis by D-Lin. G-401 cells were treated with either erastin or (1S, 3R)-RSL3 in the presence or absence of either H-Lin or D-Lin. Cells became rescued from ferroptosis upon D-Lin treatment, whereas they became more sensitive to ferroptosis upon H-Lin treatment. (F) D-Lin prevented generation of lipid peroxides. (G) D-Lin did not suppress lethality of 12 cytotoxic compounds, highlighting the specificity on ferroptosis.