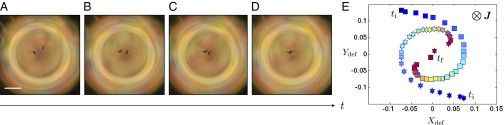
Fig. 5.
Dynamical transition from a bivalent shell into a monovalent shell. (A–D) Top-view pictures of the shell taken during the transition. In this experiment, the disclinations are located at the bottom of the shell, where it is thinnest. (E) Renormalized trajectories of the outer surface defects obtained from plotting versus , where and , respectively, designate the initial outer radius and the coordinates of the center of mass of the trajectory. The progressive color variation indicates the temporal evolution of the system, from the beginning (blue) to the end (red) of the deswelling experiment. Each symbol––star or square––is associated with one defect. (A–D) Cross-polarized images. (Scale bar, .)