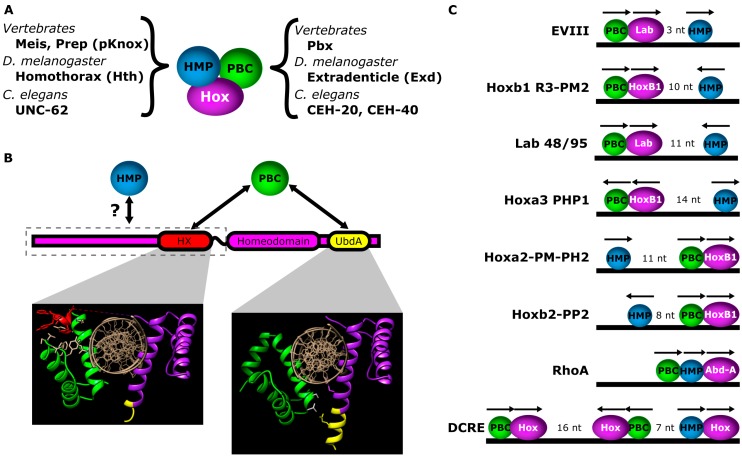
Figure 3.
Interaction between Hox factors and PBC/HMP proteins. (A) Names of PBC and HMP homeodomain proteins in C. elegans, Drosophila and vertebrates; (B) Motifs in Hox factors used to mediate interactions with PBC and HMP proteins (top). Yeast-2-hybrid data suggest sequences N-terminal to the homeodomain mediate interactions with homothorax [26]. Hox proteins can mediate interactions with PBC proteins via the HX motif or, in the case of non-vertebrate Abd-A and Ubx homologs, the UbdA motif. Structural panels: Structures produced by Foos et al., 2015, demonstrating both HX and UbdA interaction modes between Drosophila Ubx and Exd. PBC protein in green; Ubx protein in purple; HX motif in red; UbdA motif in yellow [18]. When bound to a canonical Hox-PBC binding site, Hox and PBC proteins bind on opposite sides of the DNA. Left structural panel: The HX motif (red) mediates interactions with a hydrophobic pocket formed by helix 1, helix 3 and the TALE motif of the Exd homeodomain. Right structural panel: The UbdA motif mediates interactions with helix 3 of the PBC homeodomain. UbdA can either be unstructured or form an α-helical extension of the third helix of the Hox homeodomain. Note: The Ubx protein fragment in the left panel contains both the HX and UbdA motifs, while the Ubx protein fragment in the right panel only contains the UbdA motif. (C) Examples of CRMs with Hox-PBC-HMP binding sites, demonstrating variations in the order, orientations and spacing of the binding sites. The space between HMP and Hox-PBC sites is indicated. EVIII [64]; Lab 48/95 [65]; R3-PM2 [66]; PP2 [67]; PM-PH2 [68]; PHP1 [69]; RhoA [40]; DCRE [70].