Figure 2.
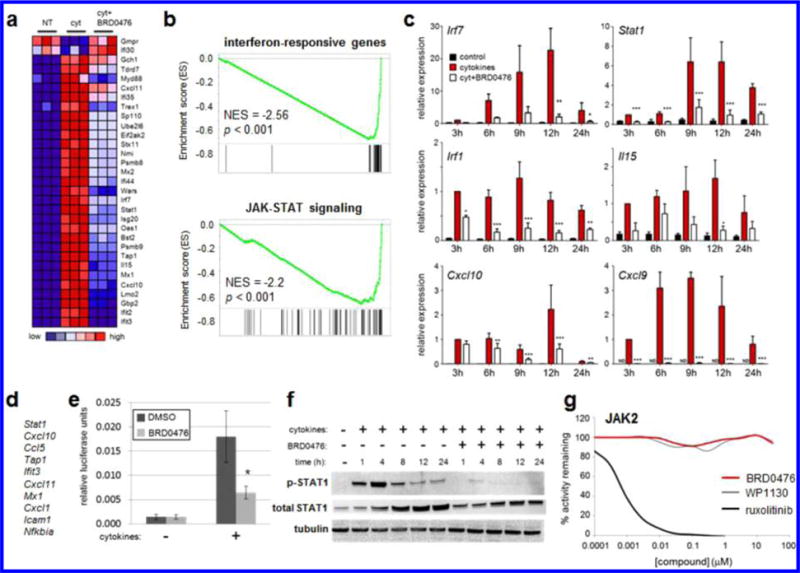
BRD0476 inhibits JAK-STAT signaling without inhibiting the kinase activity of JAK. (a) Heat map representing individual members of the top gene set, as measured by gene-set enrichment analysis, modulated by cytokines and BRD0476 after 6 h treatment in INS-1E cells. (b) Enrichment plots and scores for gene sets representing IFN-γ-responsive genes and the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. (c) Quantitative PCR of IFN-γ-responsive genes after treatment with cytokines and 10 μM BRD0476 for the indicated times in INS-1E cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 versus treatment, ANOVA with Tukey corrected t test. (d) Genes present in the leading edge of >25% enriched gene sets. (e) Gamma-activated sequence-driven luciferase activity in INS-1E cells treated for 18 h with cytokines and 10 μM BRD0476. * p < 0.0001 compared to cytokine treatment with DMSO, Student’s t test. (f) Phosphorylation of STAT1 and total STAT1 protein, as measured by Western blot, in INS-1E treated for the indicated times with cytokines and 10 μM BRD0476. Tubulin was included as a loading control. (g) Biochemical kinase activity of JAK2 in the presence of the indicated concentrations of BRD0476, WP1130, or ruxolitinib.
